Comparing tolerability and efficacy of generic versus brand alendronate: a randomized clinical study in postmenopausal women with a recent fracture
- PMID: 24205135
- PMCID: PMC3804551
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078153
Comparing tolerability and efficacy of generic versus brand alendronate: a randomized clinical study in postmenopausal women with a recent fracture
Abstract
Introduction: An increasing number of generic alendronate formulations have become available. Although expected to have the same tolerability and efficacy, head-to head comparison of generic and brand alendronate was never performed. Therefore, we compared the tolerability and efficacy of generic and brand alendronate.
Methods: In a randomized double-blinded single centre cross-over study in 37 postmenopausal women (mean age 65.4±6.4 years) with osteoporosis were treated with generic and branded alendronate during 24 (2x12) weeks. Tolerance was evaluated by the Gastro intestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) and self-reported side effects. Efficacy was assessed by serum bone turnover markers, carboxy terminal telopeptide (CTX) and procollagen type I N-terminal propeptide (PINP). No wash out period was allowed (ethical reasons). Because of possible carry over effect only data of the first 12 weeks were analyzed using linear mixed models.
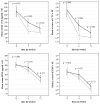
Results: There were no significant differences in overall tolerance (GSRS) between treatment groups. However, for subscale abdominal pain, patients using generic had a significantly higher mean GSRS score at week 4 (estimated mean difference (B): 0.40; 95%CI: 0.05 to 0.74, p = 0.024). The level of bone turnover markers significantly decreased over 12 weeks of follow-up for generic and branded alendronate (p < 0.001). Mean level of CTX was significantly lower with branded at week 4 (B: 121.3; 95%CI: 52.0 to 190.5), but not at week 12 (B: 53.6; 95%CI:-3.7 to 110.9). No significant differences were found for PINP at week 4 or 12.
Conclusions: Bone turnover markers were significantly reduced with branded and generic alendronate. With branded, CTX was significantly lower at 4 weeks. Generic caused significantly higher abdominal pain scores in the first 4 weeks of treatment. Therefore, generic alendronate may not have the same tolerability and efficacy as branded alendronate in the first weeks after starting treatment in patients with a recent fracture.
Trial registration: Dutch Trial Register NTR number 1867 http://www.trialregister.nl/trialreg/admin/rctview.asp?TC=1867.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Institute Dutch for Healthcare Improvement (CBO) (2011) Guideline on osteoporosis and fracture prevention, third edition. Utrecht: Nederlandse Vereniging voor Reumatologie.
-
- Huntjens KM, van Geel TA, Geusens PP, Winkens B, Willems P et al. (2011) Impact of guideline implementation by a fracture nurse on subsequent fractures and mortality in patients presenting with non-vertebral fractures. Injury 42 Suppl 4: S39-S43. doi:10.1016/S0020-1383(11)70011-0. PubMed: 21939802. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical