Growth dynamics of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a function of time to detection in BacT/alert 3D blood culture bottles with various preincubation conditions
- PMID: 24205488
- PMCID: PMC3819438
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2013.33.6.406
Growth dynamics of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a function of time to detection in BacT/alert 3D blood culture bottles with various preincubation conditions
Abstract
Background: Delayed entry of blood culture bottles is inevitable when microbiological laboratories do not operate for 24 hr. There are few studies reported for prestorage of these bottles. The growth dynamics of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa were investigated with respect to various preincubation conditions.
Methods: Fifteen or 150 colony-forming units (CFU) of bacteria were inoculated into standard aerobic or anaerobic blood culture bottles. Bottles were preincubated at 25℃ or 37℃ for 0, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, or 48 hr. The time to detection (TTD) then was monitored using the BacT/Alert 3D system (bioMerieux Inc., USA).
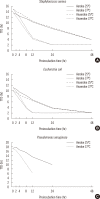
Results: Significant difference in TTD was observed following preincubation for 8 hr at 25℃ vs. 4 hr at 37℃ for S. aureus, 4 hr at 25℃ vs. 4 hr at 37℃ for E. coli, 12 hr at 25℃ vs. 4 hr at 37℃ for P. aeruginosa, compared to no preincubation (P<0.005). TTD values did not vary significantly with bacterial CFU or with aerobic or anaerobic bottle type. The BacT/Alert 3D system returned false negatives following preincubation of P. aeruginosa for 48 hr at 25℃ or 24 hr at 37℃.
Conclusions: TTD was mainly affected by preincubation temperature and duration rather than by input CFU quantity or bottle type for the 3 experimental bacteria.
Keywords: Blood culture; Detection; Preincubation; Storage.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Failure of an automated blood culture system to detect nonfermentative gram-negative bacteria.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Mar;38(3):1036-41. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.3.1036-1041.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10698992 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of 'time to detection' values between BacT/ALERT VIRTUO and BacT/ALERT 3D instruments for clinical blood culture samples.Int J Infect Dis. 2017 Sep;62:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2017.06.012. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Int J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28625838
-
Comparative study of BacT/Alert FAN bottles and standard BacT/Alert bottles.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1998 Nov;32(3):159-63. doi: 10.1016/s0732-8893(98)00094-7. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1998. PMID: 9884831
-
Predominance of Enterobacteriaceae isolates in early positive anaerobic blood culture bottles in BacT/Alert system.J Clin Lab Anal. 2013 Mar;27(2):113-20. doi: 10.1002/jcla.21571. Epub 2013 Jan 24. J Clin Lab Anal. 2013. PMID: 23349061 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative evaluation of BACT/ALERT FA PLUS and FN PLUS blood culture bottles and BD BACTEC Plus Aerobic and Anaerobic blood culture bottles for antimicrobial neutralization.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019 Dec;38(12):2229-2233. doi: 10.1007/s10096-019-03663-3. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31375943
Cited by
-
Effect of delayed entry of blood culture bottles in BACTEC automated blood culture system in the context of laboratory consolidation.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 25;12(1):1337. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05246-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35079040 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus Using Nanoemulsion-Encapsulated Zinc Phthalocyanine.Microorganisms. 2023 Apr 27;11(5):1143. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11051143. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37317117 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of 24/7 loading of blood culture bottles in a new automated incubator on the diagnosis of bloodstream infections.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021 Dec;40(12):2639-2643. doi: 10.1007/s10096-021-04283-6. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34059934
-
Using an Adenosine Triphosphate Bioluminescent Assay to Determine Effective Antibiotic Combinations against Carbapenem-Resistant Gram Negative Bacteria within 24 Hours.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 13;10(10):e0140446. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140446. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26460891 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Pre-Analytical Time on the Recovery of Pathogens from Blood Cultures: Results from a Large Retrospective Survey.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 3;12(1):e0169466. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169466. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28046040 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Principles and procedures for blood cultures; approved guidline. CLSI document M47-A. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2007.
-
- Saito T, Iinuma Y, Takakura S, Nagao M, Matsushima A, Shirano M, et al. Delayed insertion of blood culture bottles into automated continuously monitoring blood culture systems increases the time from blood sample collection to the detection of microorganisms in bacteremic patients. J Infect Chemother. 2009;15:49–53. - PubMed
-
- Viganò EF, Vasconi E, Agrappi C, Clerici P. Use of simulated blood cultures for time to detection comparison between BacT/ALERT and BACTEC 9240 blood culture systems. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2002;44:235–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

