Novel mutations of KCNQ1 in Long QT syndrome
- PMID: 24206879
- PMCID: PMC3861163
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ihj.2013.08.025
Novel mutations of KCNQ1 in Long QT syndrome
Abstract
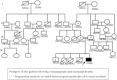
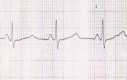
Background: Autosomal recessive Long QT syndrome is characterized by prolonged QTc along with congenital bilateral deafness depends on mutations in K(+) channel genes. A family of a Long QT syndrome proband from India has been identified with novel indel variations.
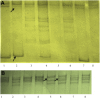
Methods: The molecular study of the proband revealed 4 novel indel variations in KCNQ1. In-silico analysis revealed the intronic variations has led to a change in the secondary structure of mRNA and splice site variations. The exonic variations leads to frameshift mutations. DNA analysis of the available family members revealed a carrier status.
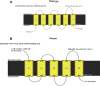
Results and conclusion: It is thus predicted that the variations may lead to a change in the position of the splicing enhancer/inhibitor in KCNQ1 leading to the formation of a truncated S2-S3 fragment of KCNQ1 transmembrane protein in cardiac cells as well as epithelial cells of inner ear leading to deafness and aberrant repolarization causing prolonged QTc.
Keywords: 3D KCNQ1 structure; Family study; JLN syndrome; Long QT syndrome; Novel mutations.
Copyright © 2013 Cardiological Society of India. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Ghosh S., Nunziato Deborah A., Pitt Geoffrey S. KCNQ1 assembly and function is blocked by long-QT syndrome mutations that disrupt interaction with calmodulin. Circ Res. 2006;98:1048–1054. - PubMed
-
- Naik A. Long QT syndrome revisited. JAPI. 2007:155. - PubMed
-
- Ma L., Lin C., Teng S. Characterization of a novel long QT syndrome mutation G52R KCNE1 in a Chinese family. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;59:612–619. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

