Design of RNA splicing analysis null models for post hoc filtering of Drosophila head RNA-Seq data with the splicing analysis kit (Spanki)
- PMID: 24209455
- PMCID: PMC3827500
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-320
Design of RNA splicing analysis null models for post hoc filtering of Drosophila head RNA-Seq data with the splicing analysis kit (Spanki)
Abstract
Background: The production of multiple transcript isoforms from one gene is a major source of transcriptome complexity. RNA-Seq experiments, in which transcripts are converted to cDNA and sequenced, allow the resolution and quantification of alternative transcript isoforms. However, methods to analyze splicing are underdeveloped and errors resulting in incorrect splicing calls occur in every experiment.
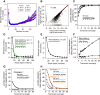
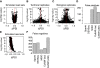
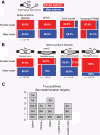
Results: We used RNA-Seq data to develop sequencing and aligner error models. By applying these error models to known input from simulations, we found that errors result from false alignment to minor splice motifs and antisense stands, shifted junction positions, paralog joining, and repeat induced gaps. By using a series of quantitative and qualitative filters, we eliminated diagnosed errors in the simulation, and applied this to RNA-Seq data from Drosophila melanogaster heads. We used high-confidence junction detections to specifically interrogate local splicing differences between transcripts. This method out-performed commonly used RNA-seq methods to identify known alternative splicing events in the Drosophila sex determination pathway. We describe a flexible software package to perform these tasks called Splicing Analysis Kit (Spanki), available at http://www.cbcb.umd.edu/software/spanki.
Conclusions: Splice-junction centric analysis of RNA-Seq data provides advantages in specificity for detection of alternative splicing. Our software provides tools to better understand error profiles in RNA-Seq data and improve inference from this new technology. The splice-junction centric approach that this software enables will provide more accurate estimates of differentially regulated splicing than current tools.
Figures



Similar articles
-
NSMAP: a method for spliced isoforms identification and quantification from RNA-Seq.BMC Bioinformatics. 2011 May 16;12:162. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-162. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21575225 Free PMC article.
-
Accurate inference of isoforms from multiple sample RNA-Seq data.BMC Genomics. 2015;16 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-S2-S15. Epub 2015 Jan 21. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25708199 Free PMC article.
-
Inference of alternative splicing from RNA-Seq data with probabilistic splice graphs.Bioinformatics. 2013 Sep 15;29(18):2300-10. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt396. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23846746 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplexed primer extension sequencing: A targeted RNA-seq method that enables high-precision quantitation of mRNA splicing isoforms and rare pre-mRNA splicing intermediates.Methods. 2020 Apr 1;176:34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.05.013. Epub 2019 May 21. Methods. 2020. PMID: 31121301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative splicing, RNA-seq and drug discovery.Drug Discov Today. 2019 Jun;24(6):1258-1267. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2019.03.030. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Drug Discov Today. 2019. PMID: 30953866 Review.
Cited by
-
Sxl-Dependent, tra/tra2-Independent Alternative Splicing of the Drosophila melanogaster X-Linked Gene found in neurons.G3 (Bethesda). 2015 Oct 28;5(12):2865-74. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.023721. G3 (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 26511498 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Analysis of Alternative Splicing in Paleopolyploid Maize.Front Plant Sci. 2017 May 10;8:694. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00694. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28539927 Free PMC article.
-
X Chromosome and Autosome Dosage Responses in Drosophila melanogaster Heads.G3 (Bethesda). 2015 Apr 7;5(6):1057-63. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.017632. G3 (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 25850426 Free PMC article.
-
Fast and accurate approximate inference of transcript expression from RNA-seq data.Bioinformatics. 2015 Dec 15;31(24):3881-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv483. Epub 2015 Aug 26. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26315907 Free PMC article.
-
A Bayesian model selection approach for identifying differentially expressed transcripts from RNA sequencing data.J R Stat Soc Ser C Appl Stat. 2018 Jan;67(1):3-23. doi: 10.1111/rssc.12213. Epub 2017 Feb 7. J R Stat Soc Ser C Appl Stat. 2018. PMID: 29353941 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

