Effects of a formal exercise program on Parkinson's disease: a pilot study using a delayed start design
- PMID: 24209458
- PMCID: PMC4030674
- DOI: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2013.10.003
Effects of a formal exercise program on Parkinson's disease: a pilot study using a delayed start design
Abstract
Introduction: Parkinson's Disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease. Increasing evidence shows that physical exercise is beneficial for motor and non-motor symptoms of PD, and animal models suggest that it may help slow progression of disease.
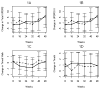
Methods: Using a randomized delayed-start design, 31 patients were randomized to an early start group (ESG) or a delayed start group (DSG) exercise program. The ESG underwent a rigorous formal group exercise program for 1 h, three days/week, for 48 weeks (November 2011-October 2012). The DSG participated in this identical exercise program from weeks 24-48. Outcome measures included the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS), Walking Test (get-up-and-go), Tinetti Mobility Test, PDQ-39 Questionnaire, and the Beck Depression Inventory.
Results: There was minimal attrition in this study, with only one patient dropping out. Results did not show improvement in total UPDRS scores with early exercise. At week 48, the mean change from baseline total UPDRS score was 6.33 in the ESG versus 5.13 in the DSG (p = 0.58). However, patients randomized to the ESG scored significantly better on the Beck Depression Inventory, with a mean improvement of 1.07 points relative to those in the DSG (p = 0.04).
Conclusions: The findings demonstrate that long-term, group exercise programs are feasible in the Parkinson's disease population, with excellent adherence and minimal drop out. While the outcome measures used in our study did not provide strong evidence that exercise has a neuroprotective effect on motor function, earlier participation in a group exercise program had a significant effect on symptoms of depression.
Keywords: Depression; Exercise; Neuroprotection; Parkinson's disease; Tinetti.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
No evidence of neuroprotection? Perhaps not...perhaps so.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014 Sep;20(9):1037. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.05.002. Epub 2014 May 14. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014. PMID: 24880962 No abstract available.
-
Response to "No evidence of neuroprotection? Perhaps not...perhaps so".Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014 Sep;20(9):1038-9. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.05.001. Epub 2014 May 20. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014. PMID: 24909315 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kowal SL, Dall TM, Chakrabarti R, Storm MV, Jain A. The current and projected economic burden of Parkinson’s disease in the United States. Mov Disord. 2013;28:311–8. - PubMed
-
- Nutt JG, Siderowf A, Guttman M, Nelson EC, Schmidt P, Zamudio J, et al. Correlates of health related quality of life (HRQL) in Parkinson’s disease (PD) [abstract] Mov Disord. 2012;27(Suppl 1):546.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical