Tula hantavirus infection in immunocompromised host, Czech Republic
- PMID: 24209605
- PMCID: PMC3837639
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1911.130421
Tula hantavirus infection in immunocompromised host, Czech Republic
Abstract
We report molecular evidence of Tula hantavirus as an etiologic agent of pulmonary-renal syndrome in an immunocompromised patient. Acute hantavirus infection was confirmed by using serologic and molecular methods. Sequencing revealed Tula virus genome RNA in the patient's blood. This case shows that Tula virus can cause serious disease in humans.
Keywords: Tula virus; hantavirus; hantavirus pulmonary syndrome; hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome; immunocompromised host; viruses.
Figures
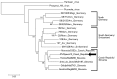
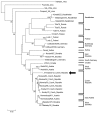
References
-
- Heroldová M, Pejčoch M, Bryja J, Jánová E, Suchomel J, Tkadlec E. Tula virus in populations of small terrestrial mammals in a rural landscape. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010;10:599–603. - PubMed
-
- Heyman P, Ceianu CS, Christova I, Tordo N, Beersma M, Alves MJ, et al. A five-year perspective on the situation of haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and status of the hantavirus reservoirs in Europe, 2005–2010. Euro Surveill. 2011;16. pii:19961. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
