Mechanisms governing metastatic dormancy and reactivation
- PMID: 24209616
- PMCID: PMC4354734
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.10.029
Mechanisms governing metastatic dormancy and reactivation
Abstract
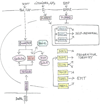
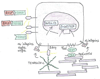
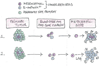
Many cancer patients suffer from metastatic relapse several years after they have undergone radical surgery. Early cancer cell dissemination followed by a protracted period of dormancy potentially explains this prevalent clinical behavior. Increasing evidence suggests that the metastasis-initiating cells are cancer stem cells or revert to this functional state upon infiltrating a target organ. Their entry into dormancy and subsequent reactivation are governed by intrinsic programs and by contextual cues, which resemble those regulating the self-renewal capability of adult stem cells. In addition, metastatic cells undergoing reactivation are nursed by specialized extracellular matrix niches, which support positive signals, such as Wnt and Notch, and attenuate negative signals, such as BMP. In spite of significant remaining uncertainties, these findings provide a framework to understand the logic of metastatic dormancy and reactivation and open new avenues for therapeutic intervention.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Aguirre-Ghiso JA, Estrada Y, Liu D, Ossowski L. ERK(MAPK) activity as a determinant of tumor growth and dormancy; regulation by p38(SAPK) Cancer Res. 2003;63:1684–1695. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Buylla A, Lim DA. For the long run: maintaining germinal niches in the adult brain. Neuron. 2004;41:683–686. - PubMed
-
- Asselin-Labat ML, Sutherland KD, Vaillant F, Gyorki DE, Wu D, Holroyd S, Breslin K, Ward T, Shi W, Bath ML, et al. Gata-3 negatively regulates the tumor-initiating capacity of mammary luminal progenitor cells and targets the putative tumor suppressor caspase-14. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011;31:4609–4622. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

