Neamine induces neuroprotection after acute ischemic stroke in type one diabetic rats
- PMID: 24211797
- PMCID: PMC3889124
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.10.071
Neamine induces neuroprotection after acute ischemic stroke in type one diabetic rats
Abstract
Introduction: Angiogenin is a member of the ribonuclease superfamily and promotes degradation of the basement membrane and the extracellular matrix. After stroke in type one diabetes (T1DM) rats, Angiogenin is significantly increased and the Angiogenin is inversely correlated with functional outcome. Neamine, an aminoglycoside antibiotic, blocks nuclear translocation of Angiogenin, thereby abolishing the biological activity of Angiogenin. In this study, we therefore investigated the effect and underlying protective mechanisms of Neamine treatment of stroke in T1DM.
Methods: T1DM was induced in male Wistar rats by streptozotocin (60mg/kg, ip), and T1DM rats were subjected to embolic middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo). Neamine (10mg/kg ip) was administered at 2, 24 and 48h after the induction of embolic MCAo. A battery of functional outcome tests was performed. Blood-brain barrier (BBB) leakage, and lesion volume were evaluated and immunostaining, and Western blot were performed.
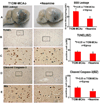
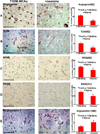
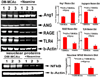
Results: Neamine treatment of stroke in T1DM rats significantly decreased BBB leakage and lesion volume as well as improved functional outcome compared to T1DM-control. Neamine also significantly decreased apoptosis and cleaved caspase-3 in the ischemic brain. Using immunostaining, we found that Neamine treatment significantly decreased nuclear Angiogenin, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NFκB) activity, advanced glycation endproducts receptor (RAGE) number, the positive area of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and increased Angeopoietin-1 expression compared to T1DM-MCAo control rats. Western blot results are consistent with the immunostaining.
Conclusion: Neamine treatment of stroke is neuroprotective in T1DM rats. Inhibition of neuroinflammatory factor expression and decrease of BBB leakage may contribute to Neamine-induced neuroprotective effects after stroke in T1DM rats.
Keywords: Ang1; Angiogenin; BBB; BP; BT; DM; ECA; ECM; IBZ; ICA; MCAo; NFκB; Neamine; PBS; RAGE; T1DM; TLR4; TUNEL; WT; advanced glycation end products receptor; angiopoietin-1; blood pressure; blood–brain barrier; body temperature; diabetes mellitus; external carotid artery; extracellular matrix; internal carotid artery; ischemic border area; mNSS; middle cerebral artery occlusion; modified neurological severity score; neuroprotection; nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; phosphate-buffered saline; stroke; terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling; toll-like receptor 4; type one diabetes; wild type.
Copyright © 2013 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Alvarez-Sabin J, Molina CA, Montaner J, Arenillas JF, Huertas R, Ribo M, Codina A, Quintana M. Effects of admission hyperglycemia on stroke outcome in reperfused tissue plasminogen activator--treated patients. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation. 2003;34:1235–1241. - PubMed
-
- Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ. Inflammatory mediators and stroke: new opportunities for novel therapeutics. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 1999;19:819–834. - PubMed
-
- Barth TM, Grant ML, Schallert T. Effects of MK-801 on recovery from sensorimotor cortex lesions. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation. 1990;21:III153–III157. - PubMed
-
- Becker KJ. Inflammation and acute stroke. Curr Opin Neurol. 1998;11:45–49. - PubMed
-
- Brott T, Lu M, Kothari R, Fagan SC, Frankel M, Grotta JC, Broderick J, Kwiatkowski T, Lewandowski C, Haley EC, Marler JR, Tilley BC. Hypertension and its treatment in the NINDS rt-PA Stroke Trial. Stroke. 1998;29:1504–1509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

