Chemical inhibition of prometastatic lysyl-tRNA synthetase-laminin receptor interaction
- PMID: 24212136
- PMCID: PMC4021855
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1381
Chemical inhibition of prometastatic lysyl-tRNA synthetase-laminin receptor interaction
Abstract
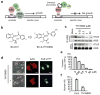
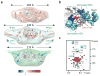
Lysyl-tRNA synthetase (KRS), a protein synthesis enzyme in the cytosol, relocates to the plasma membrane after a laminin signal and stabilizes a 67-kDa laminin receptor (67LR) that is implicated in cancer metastasis; however, its potential as an antimetastatic therapeutic target has not been explored. We found that the small compound BC-K-YH16899, which binds KRS, impinged on the interaction of KRS with 67LR and suppressed metastasis in three different mouse models. The compound inhibited the KRS-67LR interaction in two ways. First, it directly blocked the association between KRS and 67LR. Second, it suppressed the dynamic movement of the N-terminal extension of KRS and reduced membrane localization of KRS. However, it did not affect the catalytic activity of KRS. Our results suggest that specific modulation of a cancer-related KRS-67LR interaction may offer a way to control metastasis while avoiding the toxicities associated with inhibition of the normal functions of KRS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Steeg PS. Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 2006;12:895–904. - PubMed
-
- Berno V, et al. The 67 kDa laminin receptor increases tumor aggressiveness by remodeling laminin-1. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12:393–406. - PubMed
-
- Givant-Horwitz V, Davidson B, Reich R. Laminin-induced signaling in tumor cells. Cancer Lett. 2005;223:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Kim DG, et al. Interaction of two translational components, lysyl-tRNA synthetase and p40/37LRP, in plasma membrane promotes laminin-dependent cell migration. FASEB J. 2012;26:4142–4159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

