Histone variants and sensing of chromatin functional states
- PMID: 24213375
- PMCID: PMC3925688
- DOI: 10.4161/nucl.27088
Histone variants and sensing of chromatin functional states
Abstract
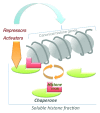
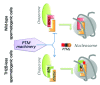
An extreme case of chromatin remodelling is the genome-wide exchange of histones with basic non-histone DNA-packaging proteins that occurs in post-meiotic male germ cells. The scale of this genome reorganization is such that chromatin needs to undergo a prior "preparation" for a facilitated action of the factors involved. Stage-specific incorporation of specialized histone variants, affecting large domains of chromatin, combined with histone post-translational modifications accompany the successive steps of the male genome reorganization. Recently, it has been shown that a testis-specific H2B variant, TH2B, one of the first identified core histone variants, replaces H2B at the time of cells' commitment into meiotic divisions and contributes to the process of global histone removal. These investigations also revealed a previously unknown histone dosage compensation mechanism that also ensures a functional interconnection between histone variant expression and histone post-translational modifications and will be further discussed here.
Keywords: acetylation; arginine methylation; crotonylation; histone chaperone; histone degradation.
Figures
Comment on
-
Chromatin-to-nucleoprotamine transition is controlled by the histone H2B variant TH2B.Genes Dev. 2013 Aug 1;27(15):1680-92. doi: 10.1101/gad.220095.113. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 23884607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rathke C, Baarends WM, Awe S, Renkawitz-Pohl R. Chromatin dynamics during spermiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
