Structural aspects of calcium-release activated calcium channel function
- PMID: 24213636
- PMCID: PMC3913758
- DOI: 10.4161/chan.26734
Structural aspects of calcium-release activated calcium channel function
Abstract
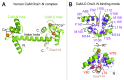
Store-operated calcium (Ca(2+)) entry is the process by which molecules located on the endo/sarcoplasmic reticulum (ER/SR) respond to decreased luminal Ca(2+) levels by signaling Ca(2+) release activated Ca(2+) channels (CRAC) channels to open on the plasma membrane (PM). This activation of PM CRAC channels provides a sustained cytosolic Ca(2+) elevation associated with myriad physiological processes. The identities of the molecules which mediate SOCE include stromal interaction molecules (STIMs), functioning as the ER/SR luminal Ca(2+) sensors, and Orai proteins, forming the PM CRAC channels. This review examines the current available high-resolution structural information on these CRAC molecular components with particular focus on the solution structures of the luminal STIM Ca(2+) sensing domains, the crystal structures of cytosolic STIM fragments, a closed Orai hexameric crystal structure and a structure of an Orai1 N-terminal fragment in complex with calmodulin. The accessible structural data are discussed in terms of potential mechanisms of action and cohesiveness with functional observations.
Keywords: Orai channel proteins; calcium release activated calcium; calmodulin; store operated calcium entry; stromal interaction molecules.
Figures
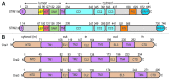
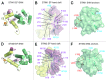
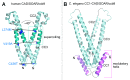
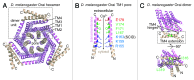
References
-
- Bootman MD, Lipp P. (2001). Calcium signalling and regulation of cell function. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences, 1-7.
-
- Berridge MJ. (2009). Cell Signalling Biology, Vol. 2009. Portland Press, Ltd., London.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
