Impact of human papillomavirus-related genital diseases on quality of life and psychosocial wellbeing: results of an observational, health-related quality of life study in the UK
- PMID: 24215264
- PMCID: PMC4225724
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-1065
Impact of human papillomavirus-related genital diseases on quality of life and psychosocial wellbeing: results of an observational, health-related quality of life study in the UK
Abstract
Background: Data on the psychosocial burden of human papillomavirus (HPV)-related diseases other than cervical cancer are scarce. The objectives of this study were to measure and compare the psychosocial burden and the impact on health-related quality of life (HRQoL) of HPV-related lower genital tract diseases and genital warts (GW) using several generic and disease-specific instruments.
Methods: Overall, 842 individuals with normal cervical cytology (n = 241), borderline nuclear abnormalities and/or mild dyskaryosis (n = 23), cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)1 (n = 84), CIN2/3 (n = 203), vulval intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN)2/3 (n = 43), GW (n = 186) and a history of GW (non-current) (n = 62) were included. The generic European Quality of Life Index Version 5D (EQ-5D) questionnaire was completed by patients with GW and VIN2/3. Sexual functioning was evaluated using the Change in Sexual Functioning Questionnaire (CSFQ). Psychosocial impact was measured in women using the HPV Impact Profile (HIP) questionnaire. HRQoL was assessed using a GW-specific questionnaire, the Cuestionario Especifico en Condilomas Acuminados (CECA) (completed by patients with GW and history of GW). For each instrument, scores were compared between groups using the Student's t-test. In addition, utility loss due to GW and VIN2/3 was evaluated by comparing mean EQ-5D scores weighted by age and sex with the UK general population normal values.
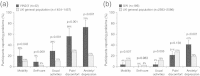
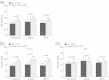
Results: A significant psychosocial impact was found in women diagnosed with HPV-related genital diseases, particularly in those with GW. The health state of younger adults with GW was significantly impaired compared with UK normal values (mean EQ-5D index score 0.86 vs 0.94, p < 0.001 for 18-24-year-olds; 0.87 vs 0.93, p = 0.030 for 25-34-year-olds). VIN2/3 was found to have a significant negative impact on sexual functioning, and women with VIN2/3 had a highly impaired health state compared with women in the UK general population (weighted mean EQ-5D index score 0.72 vs 0.89, p < 0.001; weighted mean Visual Analogue Scale score 62 vs 85, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: HPV-related lower genital tract lesions and GW significantly impair psychosocial wellbeing and HRQoL. The psychosocial aspects of HPV-related diseases need to be considered when evaluating the potential benefit of HPV vaccination.
Figures


References
-
- Koutsky L. Epidemiology of genital human papillomavirus infection. Am J Med. 1997;102:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Lacey CJN, Lowndes CM, Shah KV. Chapter 4: Burden and management of non-cancerous HPV-related conditions: HPV-6/11 disease. Vaccine. 2006;24(Suppl 3):35–41. - PubMed
-
- Wieland U, Pfister H. In: Human Papillomavirus Infection: A clinical Atlas. Gross GE, Barrasso R, editor. Berlin: Ullstein Mosby; 1997. Papillomaviruses in human pathology: epidemiology, pathogenesis and oncogenic role; pp. 1–18.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

