Alternate day fasting for weight loss in normal weight and overweight subjects: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 24215592
- PMCID: PMC3833266
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2891-12-146
Alternate day fasting for weight loss in normal weight and overweight subjects: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Alternate day fasting (ADF; ad libitum "feed day", alternated with 25% energy intake "fast day"), is effective for weight loss and cardio-protection in obese individuals. Whether these effects occur in normal weight and overweight individuals remains unknown. This study examined the effect of ADF on body weight and coronary heart disease risk in non-obese subjects.
Methods: Thirty-two subjects (BMI 20-29.9 kg/m2) were randomized to either an ADF group or a control group for 12 weeks.
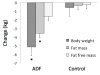
Results: Body weight decreased (P < 0.001) by 5.2 ± 0.9 kg (6.5 ± 1.0%) in the ADF group, relative to the control group, by week 12. Fat mass was reduced (P < 0.001) by 3.6 ± 0.7 kg, and fat free mass did not change, versus controls. Triacylglycerol concentrations decreased (20 ± 8%, P < 0.05) and LDL particle size increased (4 ± 1 Å, P < 0.01) in the ADF group relative to controls. CRP decreased (13 ± 17%, P < 0.05) in the ADF group relative to controls at week 12. Plasma adiponectin increased (6 ± 10%, P < 0.01) while leptin decreased (40 ± 7%, P < 0.05) in the ADF group versus controls by the end of the study. LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, homocysteine and resistin concentrations remained unchanged after 12 weeks of treatment.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that ADF is effective for weight loss and cardio-protection in normal weight and overweight adults, though further research implementing larger sample sizes is required before solid conclusion can be reached.
Figures
References
-
- Varady KA, Hellerstein MK. Alternate-day fasting and chronic disease prevention: a review of human and animal trials. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:7–13. - PubMed
-
- Bhutani S, Klempel MC, Kroeger CM, Trepanowski JF, Varady KA. Alternate day fasting and endurance exercise combine to reduce body weight and favorably alter plasma lipids in obese humans. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2013. Epub ahead of print. - PubMed
-
- Heilbronn LK, Smith SR, Martin CK, Anton SD, Ravussin E. Alternate-day fasting in nonobese subjects: effects on body weight, body composition, and energy metabolism. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;81:69–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

