Antimalarial drug discovery - approaches and progress towards new medicines
- PMID: 24217412
- PMCID: PMC3941073
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro3138
Antimalarial drug discovery - approaches and progress towards new medicines
Erratum in
- Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014 Jan;12(1):70
-
Antimalarial drug discovery - approaches and progress towards new medicines.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017 Sep;15(9):572. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2017.88. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28736448 No abstract available.
Abstract
Malaria elimination has recently been reinstated as a global health priority but current therapies seem to be insufficient for the task. Elimination efforts require new drug classes that alleviate symptoms, prevent transmission and provide a radical cure. To develop these next-generation medicines, public-private partnerships are funding innovative approaches to identify compounds that target multiple parasite species at multiple stages of the parasite life cycle. In this Review, we discuss the cell-, chemistry- and target-based approaches used to discover new drug candidates that are currently in clinical trials or undergoing preclinical testing.
Figures
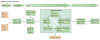
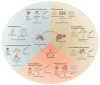
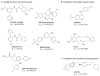
References
-
- WHO. World Malaria Report 2012. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2012. pp. 1–276.
-
- Murray CJ, et al. Global malaria mortality between 1980 and 2010: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2012;379:413–31. This analysis is noteworthy in that it suggests that the number of malaria fatalities are underreported by the World Health Organization. - PubMed
-
- Beutler E. The hemolytic effect of primaquine and related compounds: a review. Blood. 1959;14:103–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

