Cellular senescence mediated by p16INK4A-coupled miRNA pathways
- PMID: 24217920
- PMCID: PMC3919591
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt1096
Cellular senescence mediated by p16INK4A-coupled miRNA pathways
Abstract
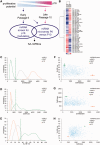
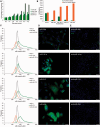
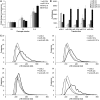
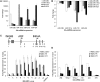
p16 is a key regulator of cellular senescence, yet the drivers of this stable state of proliferative arrest are not well understood. Here, we identify 22 senescence-associated microRNAs (SA-miRNAs) in normal human mammary epithelial cells. We show that SA-miRNAs-26b, 181a, 210 and 424 function in concert to directly repress expression of Polycomb group (PcG) proteins CBX7, embryonic ectoderm development (EED), enhancer of zeste homologue 2 (EZH2) and suppressor of zeste 12 homologue (Suz12), thereby activating p16. We demonstrate the existence of a tight positive feedback loop in which SA-miRNAs activate and re-enforce the expression of other SA-miRNA members. In contrast, PcG members restrain senescence by epigenetically repressing the expression of these SA-miRNAs. Importantly, loss of p16 leads to repression of SA-miRNA expression, intimately coupling this effector of senescence to the SA-miRNA/PcG self-regulatory loop. Taken together, our findings illuminate an important regulatory axis that underpins the transition from proliferation to cellular senescence.
Figures


References
-
- Hayflick L. The limited in vitro lifetime of human diploid cell strains. Exp. Cell Res. 1965;37:614–636. - PubMed
-
- Michaloglou C, Vredeveld LC, Soengas MS, Denoyelle C, Kuilman T, van der Horst CM, Majoor DM, Shay JW, Mooi WJ, Peeper DS. BRAFE600-associated senescence-like cell cycle arrest of human naevi. Nature. 2005;436:720–724. - PubMed
-
- Campisi J, d'Adda di Fagagna F. Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:729–740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

