Etiopathogenesis of recurrent aphthous stomatitis and the role of immunologic aspects: literature review
- PMID: 24217985
- PMCID: PMC4024130
- DOI: 10.1007/s00005-013-0261-y
Etiopathogenesis of recurrent aphthous stomatitis and the role of immunologic aspects: literature review
Abstract
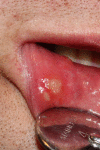
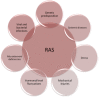
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS; recurrent aphthous ulcers; canker sores) belongs to the group of chronic, inflammatory, ulcerative diseases of the oral mucosa. Up to now, the etiopathogenesis of this condition remains unclear; it is, however, considered to be multifactorial. The results of currently performed studies indicate that genetically mediated disturbances of the innate and acquired immunity play an important role in the disease development. Factors that modify the immunologic response in RAS include: food allergies, vitamin and microelement deficiencies, hormonal and gastrointestinal disorders (e.g., celiac disease, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis), some viral and bacterial infections, mechanical injuries and stress. In this paper, we presented the main etiopathogenetic factors of RAS with a special emphasis on the mechanisms of the immune response modification. Moreover, we discussed the crucial clinical symptoms and types of RAS together with epidemiologic data based on the current medical literature reports and our own observations.
Figures
References
-
- Akman A, Sallakci N, Coskun M, et al. TNF-α gene 1031 T/C polymorphism in Turkish patients with Behçet’s disease. Br J Dermatol. 2006;155:350–356. - PubMed
-
- Akman A, Ekinci NC, Karcaroglu H, et al. Relationship between periodontal findings and specific polymorphisms of interleukin-1α and -1β in Turkish patients with Behçet’s disease. Arch Dermatol Res. 2008;300:19–26. - PubMed
-
- Albanidou-Farmaki E, Kayavis IG, Polymenidis Z, et al. HLA-A, B, C, and DR antigens in recurrent oral ulcers. Ann Dent. 1988;47:5–8. - PubMed
-
- Albanidou-Farmaki E, Markopoulos AK, Kalogerakou F, et al. Detection, enumeration and characterization of T helper cells secreting type 1 and type 2 cytokines in patients with recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2007;212:101–105. - PubMed
-
- Albanidou-Farmaki E, Deligiannidis A, Markopoulos AK, et al. HLA haplotypes in recurrent aphthous stomatitis: a mode of inheritance? Int J Immunogenet. 2008;35:427–432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical