Computerized advice on drug dosage to improve prescribing practice
- PMID: 24218045
- PMCID: PMC11393523
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002894.pub3
Computerized advice on drug dosage to improve prescribing practice
Abstract
Background: Maintaining therapeutic concentrations of drugs with a narrow therapeutic window is a complex task. Several computer systems have been designed to help doctors determine optimum drug dosage. Significant improvements in health care could be achieved if computer advice improved health outcomes and could be implemented in routine practice in a cost-effective fashion. This is an updated version of an earlier Cochrane systematic review, first published in 2001 and updated in 2008.
Objectives: To assess whether computerized advice on drug dosage has beneficial effects on patient outcomes compared with routine care (empiric dosing without computer assistance).
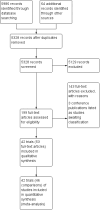
Search methods: The following databases were searched from 1996 to January 2012: EPOC Group Specialized Register, Reference Manager; Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, Ovid; EMBASE, Ovid; and CINAHL, EbscoHost. A "top up" search was conducted for the period January 2012 to January 2013; these results were screened by the authors and potentially relevant studies are listed in Studies Awaiting Classification. The review authors also searched reference lists of relevant studies and related reviews.
Selection criteria: We included randomized controlled trials, non-randomized controlled trials, controlled before-and-after studies and interrupted time series analyses of computerized advice on drug dosage. The participants were healthcare professionals responsible for patient care. The outcomes were any objectively measured change in the health of patients resulting from computerized advice (such as therapeutic drug control, clinical improvement, adverse reactions).
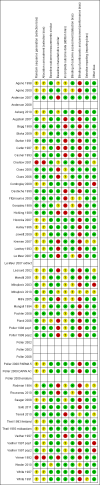
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted data and assessed study quality. We grouped the results from the included studies by drug used and the effect aimed at for aminoglycoside antibiotics, amitriptyline, anaesthetics, insulin, anticoagulants, ovarian stimulation, anti-rejection drugs and theophylline. We combined the effect sizes to give an overall effect for each subgroup of studies, using a random-effects model. We further grouped studies by type of outcome when appropriate (i.e. no evidence of heterogeneity).
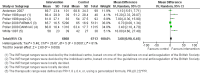
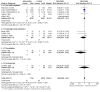
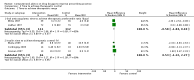
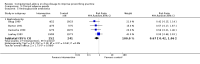
Main results: Forty-six comparisons (from 42 trials) were included (as compared with 26 comparisons in the last update) including a wide range of drugs in inpatient and outpatient settings. All were randomized controlled trials except two studies. Interventions usually targeted doctors, although some studies attempted to influence prescriptions by pharmacists and nurses. Drugs evaluated were anticoagulants, insulin, aminoglycoside antibiotics, theophylline, anti-rejection drugs, anaesthetic agents, antidepressants and gonadotropins. Although all studies used reliable outcome measures, their quality was generally low.This update found similar results to the previous update and managed to identify specific therapeutic areas where the computerized advice on drug dosage was beneficial compared with routine care:1. it increased target peak serum concentrations (standardized mean difference (SMD) 0.79, 95% CI 0.46 to 1.13) and the proportion of people with plasma drug concentrations within the therapeutic range after two days (pooled risk ratio (RR) 4.44, 95% CI 1.94 to 10.13) for aminoglycoside antibiotics;2. it led to a physiological parameter more often within the desired range for oral anticoagulants (SMD for percentage of time spent in target international normalized ratio +0.19, 95% CI 0.06 to 0.33) and insulin (SMD for percentage of time in target glucose range: +1.27, 95% CI 0.56 to 1.98);3. it decreased the time to achieve stabilization for oral anticoagulants (SMD -0.56, 95% CI -1.07 to -0.04);4. it decreased the thromboembolism events (rate ratio 0.68, 95% CI 0.49 to 0.94) and tended to decrease bleeding events for anticoagulants although the difference was not significant (rate ratio 0.81, 95% CI 0.60 to 1.08). It tended to decrease unwanted effects for aminoglycoside antibiotics (nephrotoxicity: RR 0.67, 95% CI 0.42 to 1.06) and anti-rejection drugs (cytomegalovirus infections: RR 0.90, 95% CI 0.58 to 1.40);5. it tended to reduce the length of time spent in the hospital although the difference was not significant (SMD -0.15, 95% CI -0.33 to 0.02) and to achieve comparable or better cost-effectiveness ratios than usual care;6. there was no evidence of differences in mortality or other clinical adverse events for insulin (hypoglycaemia), anaesthetic agents, anti-rejection drugs and antidepressants.For all outcomes, statistical heterogeneity quantified by I(2) statistics was moderate to high.
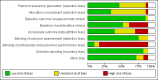
Authors' conclusions: This review update suggests that computerized advice for drug dosage has some benefits: it increases the serum concentrations for aminoglycoside antibiotics and improves the proportion of people for which the plasma drug is within the therapeutic range for aminoglycoside antibiotics.It leads to a physiological parameter more often within the desired range for oral anticoagulants and insulin. It decreases the time to achieve stabilization for oral anticoagulants. It tends to decrease unwanted effects for aminoglycoside antibiotics and anti-rejection drugs, and it significantly decreases thromboembolism events for anticoagulants. It tends to reduce the length of hospital stay compared with routine care while comparable or better cost-effectiveness ratios were achieved.However, there was no evidence that decision support had an effect on mortality or other clinical adverse events for insulin (hypoglycaemia), anaesthetic agents, anti-rejection drugs and antidepressants. In addition, there was no evidence to suggest that some decision support technical features (such as its integration into a computer physician order entry system) or aspects of organization of care (such as the setting) could optimize the effect of computerized advice.Taking into account the high risk of bias of, and high heterogeneity between, studies, these results must be interpreted with caution.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
































Update of
-
Computerized advice on drug dosage to improve prescribing practice.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD002894. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002894.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Nov 12;(11):CD002894. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002894.pub3. PMID: 18646085 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Ageno 1998 {published data only}
-
- Ageno W, Turpie AG. A randomized comparison of a computer‐based dosing program with a manual system to monitor oral anticoagulant therapy. Thrombosis Research 1998;91(5):237‐40. - PubMed
Ageno 2000 {published data only}
-
- Ageno W, Johnson J, Nowacki B, Turpie AG. A computer generated induction system for hospitalized patients starting on oral anticoagulant therapy. Thrombosis & Haemostasis 2000;83(6):849‐52. [0340‐6245] - PubMed
Anderson 2007 {published data only}
-
- Anderson JL, Horne BD, Stevens SM, Grove AS, Barton S, et al. Randomized trial of genotype‐guided versus standard warfarin dosing in patients initiating oral anticoagulation. Circulation 2007;116(22):2563‐70. - PubMed
Anderson 2008 {published data only}
-
- Anderson JL. A double blind randomised trial of genotype guided versus standard warfarin dosing in patients initiated on oral anticoagulation: the COUMAGEN study. Clinical Research in Cardiology 2008;97:8.
Asberg 2010 {published data only}
-
- Asberg A, Falck P, Undset LH, Dorje C, Holdaas H, Hartmann A, et al. Computer‐assisted cyclosporine dosing performs better than traditional dosing in renal transplant recipients: results of a pilot study. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 2010;32(2):152‐8. - PubMed
Augstein 2007 {published data only}
-
- Augstein P, Vogt L, Kohnert KD, Freyse EJ, Heinke P, Salzsieder E. Outpatient assessment of Karlsburg Diabetes Management System‐based decision support. Diabetes Care 2007;30(7):1704‐8. - PubMed
Begg 1989 {published data only}
Blaha 2009 {published data only}
Burton 1991 {published data only}
-
- Burton ME, Ash CL, Hill DPJ, Handy T, Shepherd MD, Vasko MR. A controlled trial of the cost benefit of computerized Bayesian aminoglycoside administration. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1991;49(6):685‐94. - PubMed
Carter 1987 {published data only}
-
- Carter BL, Taylor JW, Becker A. Evaluation of three dosage‐prediction methods for initial in‐hospital stabilization of warfarin therapy. Clinical Pharmacy 1987;6(1):37‐45. - PubMed
Casner 1993 {published data only}
-
- Casner PR, Reilly R, Ho H. A randomized controlled trial of computerized pharmacokinetic theophylline dosing versus empiric physician dosing. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1993;53(6):684‐90. - PubMed
Chertow 2001 {published data only}
-
- Chertow GM, Lee J, Kuperman GJ, Burdick E, Horsky J, Seger DL, et al. Guided medication dosing for inpatients with renal insufficiency. JAMA 2001;286(22):2839‐44. - PubMed
Claes 2005 {published data only}
-
- Claes N, Buntinx F, Vijgen J, Arnout J, Vermylen J, Fieuws S, et al. The Belgian Improvement Study on Oral Anticoagulation Therapy: a randomized clinical trial. European H eart Journal 2005;26:2159‐65. - PubMed
Claes 2006 {published data only}
-
- Claes N, Moeremans K, Frank B, Jef A, Jos V, Herman VL, et al. Estimating the cost‐effectiveness of quality‐improving interventions in oral anticoagulation management within general practice. Value in Health 2006;9:369‐76. - PubMed
Cordingley 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cordingley JJ, Vlasselaers D, Dormand NC, Wouters PJ, Squire SD, Chassin LJ, et al. Intensive insulin therapy: enhanced Model Predictive Control algorithm versus standard care. Intensive Care Medicine 2009;35(1):123‐8. - PubMed
Destache 1990 {published data only}
-
- Destache CJ, Meyer SK, Bittner MJ, Hermann KG. Impact of a clinical pharmacokinetic service on patients treated with aminoglycosides: a cost‐benefit analysis. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 1990;12(5):419‐26. - PubMed
Fitzmaurice 2000 {published data only}
-
- Fitzmaurice DA, Hobbs FD, Murray ET, Holder RL, Allan TF, Rose PE. Oral anticoagulation management in primary care with the use of computerized decision support and near‐patient testing: a randomized, controlled trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2000;160(15):2343‐8. - PubMed
Gonzalez 1989 {published data only}
-
- Gonzalez ER, Vanderheyden BA, Ornato JP, Comstock TG. Computer‐assisted optimization of aminophylline therapy in the emergency department. American Journal of Emergency Medicine 1989;7(4):395‐401. - PubMed
Hickling 1989 {published data only}
-
- Hickling K, Begg E, Moore ML. A prospective randomised trial comparing individualised pharmacokinetic dosage prediction for aminoglycosides with prediction based on estimated creatinine clearance in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Medicine 1989;15(4):233‐7. - PubMed
Hovorka 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hovorka R, Kremen J, Blaha J, Matias M, Anderlova K, Bosanska L, et al. Blood glucose control by a model predictive control algorithm with variable sampling rate versus a routine glucose management protocol in cardiac surgery patients: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2007;92:2960‐4. - PubMed
Hurley 1986 {published data only}
-
- Hurley SF, Dziukas LJ, McNeil JJ, Brignell MJ. A randomized controlled clinical trial of pharmacokinetic theophylline dosing. American Review of Respiratory Disease 1986;134(6):1219‐24. - PubMed
Jowett 2009 {published data only}
-
- Jowett S, Bryan S, Poller L, Besselaar AMHP, Meer FJM, Palareti G, et al. The cost‐effectiveness of computer‐assisted anticoagulant dosage: results from the European Action on Anticoagulation (EAA) multicentre study. Journal of Thrombosis & Haemostasis 2009; Vol. 7, issue 9:1482‐90. - PubMed
Kremen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kremen J, Blaha J, Kopecky P, Bosansk L, Kotrlikova E, Roubicek T, et al. The treatment of hyperglycaemia in critically ill patients: comparison of standard protocol and computer algorithm [In Czech] . Vnitrni Lekarstvi 2007;53(12):1269‐73. - PubMed
Leehey 1993 {published data only}
-
- Leehey DJ, Braun BI, Tholl DA, Chung LS, Gross CA, Roback JA, et al. Can pharmacokinetic dosing decrease nephrotoxicity associated with aminoglycoside therapy. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1993;4:81‐90. - PubMed
Le Meur 2007 {published data only}
-
- Meur Y, Buchler M, Thierry A, Caillard S, Villemain F, Lavaud S, et al. Individualized mycophenolate mofetil dosing based on drug exposure significantly improves patient outcomes after renal transplantation. American Journal of Transplantation 2007;7(11):2496‐503. [1600‐6135] - PubMed
Le Meur 2007 extract {published data only}
-
- Individualized dosing of MMF is superior to fixed dosing in renal transplant patients. Nature Clinical Practice Nephrology 2008; Vol. 4, issue 1:9. [1745‐8323]
Lesourd 2002 {published data only}
-
- Lesourd F, Avril C, Boujennah A, Parinaud J. A computerized decision support system for ovarian stimulation by gonadotropins. Fertility and Sterility 2002;77(3):456‐60. - PubMed
Manotti 2001 {published data only}
-
- Manotti C, Moia M, Palareti G, Pengo V, Ria L, Dettori AG. Effect of computer‐aided management on the quality of treatment in anticoagulated patients: a prospective, randomized, multicenter trial of APROAT (Automated Program for Oral Anticoagulant Treatment). Haematologica 2001;86(10):1060‐70. - PubMed
Mihajlovic 2003 {published data only}
-
- Mihajlovic GS, Milovanovic DR, Jankovic SM. Comparison of efficacy and safety between individualized and empiric dose regimen of amitriptyline in the treatment of major depressive episode. Psychiatry & Clinical Neurosciences 2003;57(6):580‐5. [1323‐1316] - PubMed
Mihajlovic 2010 {published data only}
-
- Mihajlovic G, Djukic‐Dejanovic S, Jovanovic‐Mihajlovic N, Jankovic S, Janjic V, Jovanovic M, et al. Comparison of safety between individualized and empiric dose regimen of amitriptyline in the treatment of major depressive episode. Psychiatria Danubina 2010; Vol. 22, issue 2:354‐7. [0353‐5053] - PubMed
Mitra 2005 {published data only}
-
- Mitra R, Marciello MA, Brain C, Ahangar B, Burke DT. Efficacy of computer‐aided dosing of warfarin among patients in a rehabilitation hospital. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2005;84(6):423‐7. [0894‐9115] - PubMed
Mungall 1994 {published data only}
-
- Mungall DR, Anbe D, Forrester PL, Luoma T, Genovese R, Mahan J, et al. A prospective randomized comparison of the accuracy of computer‐assisted versus GUSTO nomogram‐‐directed heparin therapy. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1994;55(5):591‐6. - PubMed
Pachler 2008 {published data only}
-
- Pachler C, Plank J, Weinhandl H, Chassin LJ, Wilinska ME, Kulnik R, et al. Tight glycaemic control by an automated algorithm with time‐variant sampling in medical ICU patients. Intensive Care Medicine 2008;34(7):1224‐30. [0342‐4642] - PubMed
Plank 2006 {published data only}
-
- Plank J, Blaha J, Cordingley J, Wilinska ME, Chassin LJ, Morgan C, et al. Multicentric, randomized, controlled trial to evaluate blood glucose control by the model predictive control algorithm versus routine glucose management protocols in intensive care unit patients. Diabetes Care 2006;29(2):271‐6. [0149‐5992] - PubMed
Poller 1998 pop1 {published data only}
-
- Poller L, Shiach CR, MacCallum PK, Johansen AM, Munster AM, Magalhaes A, et al. Multicentre randomised study of computerised anticoagulant dosage. European Concerted Action on Anticoagulation. Lancet 1998;352(9139):1505‐9. - PubMed
Poller 1998 pop2 {published data only}
-
- Poller L, Shiach CR, MacCallum PK, Johansen AM, Munster AM, Magalhaes A, et al. Multicentre randomised study of computerised anticoagulant dosage. European Concerted Action on Anticoagulation. Lancet 1998;352(9139):1505‐9. - PubMed
Poller 2002 {published data only}
-
- Poller L. European Concerted Action on Anticoagulation (ECAA): studies on computer‐assisted anticoagulant dosage. Turkish Journal of Haematology 2002;19(2):179‐84. [1300‐7777] - PubMed
Poller 2003 {published data only}
-
- Poller L, Jespersen J, Tripodi A, Besselaar AMHP, Mer FJM, Shiac C, et al. European Action on Anti‐coagulation ‐ cost effectiveness of computer assisted anti‐coagulant dosage. Journal of Thrombosis & Haemostasis 2003;1(Suppl 1):Abstract.
Poller 2008 {published data only}
-
- Poller L, Keown M, Ibrahim S, Lowe G, Moia M, Turpie AG, et al. An international multicenter randomized study of computer‐assisted oral anticoagulant dosage vs. medical staff dosage. Journal of Thrombosis & Haemostasis 2008; Vol. 6, issue 6:935‐43. - PubMed
Poller 2008 PARMA 5 {published data only}
-
- Poller L, Keown M, Ibrahim S, Lowe G, Moia M, Turpie AG, et al. A multicentre randomised clinical endpoint study of PARMA 5 computer‐assisted oral anticoagulant dosage. British Journal of Haematology 2008; Vol. 143, issue 2:274‐83. - PubMed
Poller 2009 DAWN AC {published data only}
-
- Poller L, Keown M, Ibrahim S, Lowe G, Moia M, Turpie AG, et al. A multicentre randomised assessment of the DAWN AC computer‐assisted oral anticoagulant dosage program. Thrombosis & Haemostasis 2009;101(3):487‐94. [0340‐6245] - PubMed
Poller 2009 erratum {published data only}
-
- Poller. Erratum: A multicentre randomised assessment of the DAWN AC computer‐assisted oral anticoagulant dosage program (Thrombosis and Haemostasis (2009) 101 (487‐494)). Thrombosis and Haemostasis 2009;101(4):794. [0340‐6245] - PubMed
Rodman 1984 {published data only}
-
- Rodman JH, Jelliffe RW, Kolb E, Tuey DB, Guzman MF, Wagers PW, et al. Clinical studies with computer‐assisted initial lidocaine therapy. Archives of Internal Medicine 1984;144(4):703‐9. - PubMed
Rousseau 2010 {published data only}
-
- Rousseau A, Laroche M‐L, Venisse N, Loichot‐Roselmac C, Turcant A, Hoizey G, et al. Cost‐effectiveness analysis of individualized mycophenolate mofetil dosing in kidney transplant patients in the APOMYGRE trial. Transplantation 2010; Vol. 89, issue 10:1255‐62. - PubMed
Saager 2008 {published data only}
-
- Saager L, Collins GL, Burnside B, Tymkew H, Zhang L, Jacobsohn E, et al. A randomized study in diabetic patients undergoing cardiac surgery comparing computer‐guided glucose management with a standard sliding scale protocol. Journal of Cardiothoracic & Vascular Anesthesia 2008; Vol. 22, issue 3:377‐82. - PubMed
Sato 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sato T, Carvalho G, Sato H, Lattermann R, Schricker T. Glucose and insulin administration while maintaining normoglycemia during cardiac surgery using a computer‐assisted algorithm. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics 2011;13:79‐84. - PubMed
Terrell 2010 {published data only}
-
- Terrell KM, Perkins AJ, Hui SL, Callahan CM, Dexter PR, Miller DK. Computerized decision support for medication dosing in renal insufficiency: a randomized, controlled trial. Annals of Emergency Medicine 2010; Vol. 56, issue 6:623‐9. - PubMed
Theil 1993 fentanyl {published data only}
-
- Theil DR, Stanley TE 3rd, White WD, Goodman DK, Glass PS, Bai SA, et al. Midazolam and fentanyl continuous infusion anesthesia for cardiac surgery: a comparison of computer‐assisted versus manual infusion systems. Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia 1993;7(3):300‐6. - PubMed
Theil 1993 midazolam {published data only}
-
- Theil DR, Stanley TE 3rd, White WD, Goodman DK, Glass PS, Bai SA, et al. Midazolam and fentanyl continuous infusion anesthesia for cardiac surgery: a comparison of computer‐assisted versus manual infusion systems. Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia 1993;7(3):300‐6. - PubMed
Vadher 1997 {published data only}
Vadher 1997 pop1 {published data only}
-
- Vadher BD, Patterson DL, Leaning M. Comparison of oral anticoagulant control by a nurse‐practitioner using a computer decision‐support system with that by clinicians. Clinical and Laboratory Haematology 1997;19(3):203‐7. - PubMed
Vadher 1997 pop2 {published data only}
-
- Vadher BD, Patterson DL, Leaning M. Comparison of oral anticoagulant control by a nurse‐practitioner using a computer decision‐support system with that by clinicians. Clinical and Laboratory Haematology 1997;19(3):203‐7. - PubMed
Verner 1992 {published data only}
-
- Verner D, Seligmann H, Platt S, Dany S, Almog S, Zulty L, et al. Computer assisted design of a theophylline dosing regimen in acute bronchospasm: serum concentrations and clinical outcome. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1992;43(1):29‐33. - PubMed
Wexler 2010 {published data only}
White 1987 {published data only}
-
- White RH, Hong R, Venook AP, Daschbach MM, Murray W, Mungall DR, et al. Initiation of warfarin therapy: comparison of physician dosing with computer‐assisted dosing. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1987;2(3):141‐8. - PubMed
White 1991 {published data only}
-
- White RH, Mungall D. Outpatient management of warfarin therapy: comparison of computer‐predicted dosage adjustment to skilled professional care. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 1991;13(1):46‐50. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abbrecht 1982 {published data only}
-
- Abbrecht PH, O'Leary TJ, Behrendt DM. Evaluation of a computer‐assisted method for individualized anticoagulation: retrospective and prospective studies with a pharmacodynamic model. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1982;32(1):129‐36. - PubMed
Absalom 2003 {published data only}
-
- Absalom AR, Kenny GNC. Closed‐loop control of propofol anaesthesia using bispectral index: performance assessment in patients receiving computer‐controlled propofol and manually controlled remifentanil infusions for minor surgery. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2003;90(6):737‐41. [0007‐0912] - PubMed
Albisser 2007 {published data only}
-
- Albisser AM, Wright CE, Sakkal S. Averting iatrogenic hypoglycemia through glucose prediction in clinical practice: progress towards a new procedure in diabetes. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2007;76:207‐14. - PubMed
Alvis 1985 {published data only}
-
- Alvis JM, Reves JG, Govier AV, Menkhaus PG, Henling CE, Spain JA, et al. Computer‐assisted continuous infusions of fentanyl during cardiac anesthesia: comparison with a manual method. Anesthesiology 1985;63(1):41–9. - PubMed
Barletta 2009 {published data only}
-
- Barletta J, McAllen K, Eriksson E, Thayer S, Deines G, Blau S, et al. The effect of a computer‐assisted insulin infusion protocol on glucose control and variability in a surgical intensive care unit. Critical Care Medicine 2009:A25. [0090‐3493]
Barras 2008 {published data only}
-
- Barras MA, Duffull SB, Atherton JJ, Green B. Individualized compared with conventional dosing of enoxaparin. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2008;83(6):882‐8. - PubMed
Barras 2010 {published data only}
-
- Barras MA, Duffull SB, Atherton JJ, Green B. Individualized dosing of enoxaparin for subjects with renal impairment is superior to conventional dosing at achieving therapeutic concentrations. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 2010;32(4):482‐8. - PubMed
Bartal 2003 {published data only}
-
- Bartal C, Danon A, Schlaeffer F, Reisenberg K, Alkan M, Smoliakov R, et al. Pharmacokinetic dosing of aminoglycosides: a controlled trial. American Journal of Medicine 2003;114:194‐8. - PubMed
Berg 2009 {published data only}
-
- Berg T, Weich V, Teuber G, Klinker H, Moller B, Rasenack J, et al. Individualized treatment strategy according to early viral kinetics in hepatitis C virus type 1‐infected patients. Hepatology 2009;50(2):369‐77. - PubMed
Burger 2003 {published data only}
-
- Burger D, Hugen P, Reiss P, Gyssens I, Schneider M, Kroon F, et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring of nelfinavir and indinavir in treatment‐naive HIV‐1‐infected individuals. AIDS 2003;17(8):1157‐65. [0269‐9370] - PubMed
Bury 2005 {published data only}
-
- Bury J, Hurt C, Roy A, Cheesman L, Bradburn M, Cross S, et al. LISA: a web‐based decision‐support system for trial management of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. British Journal of Haematology 2005;129(6):746‐54. - PubMed
Caraballo 2008 {published data only}
-
- Caraballo PJ, North F, Peters S, Puffer M, Nyman M, Epps S, et al. Use of decision support to prevent errors when documenting height and weight in the hospital electronic medical record. AMIA 2008; Vol. Annual Symposium Proceedings/AMIA Symposium :890. - PubMed
Carter 1987a {published data only}
-
- Carter BL, Taylor JW, Becker A. Evaluation of three dosage‐prediction methods for initial in‐hospital stabilization of warfarin therapy. Clinical Pharmacy 1987;6(1):37‐45. - PubMed
Cavalcanti 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cavalcanti AB, Silva E, Pereira AJ, Caldeira‐Filho M, Almeida FP, Westphal GA, et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing a computer‐assisted insulin infusion protocol with a strict and a conventional protocol for glucose control in critically ill patients. Journal of Critical Care 2009;24:371‐8. - PubMed
Chan 2006 {published data only}
-
- Chan ALF, Wang H‐Y, Leung HWC. Incorporation of a gentamicin dosage calculator into a computerized prescriber‐order‐entry system. American Journal of Health‐System Pharmacy 2006;63(14):1344‐5. [1079‐2082] - PubMed
Chiarelli 1990 {published data only}
-
- Chiarelli F, Tumini S, Morgese G, Albisser AM. Controlled study in diabetic children comparing insulin‐dosage adjustment by manual and computer algorithms. Diabetes Care 1990;13(10):1080‐4. - PubMed
Cohen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cohen P, Rogol AD, Howard CP, Bright GM, Kappelgaard A‐M, Rosenfeld RG, et al. Insulin growth factor‐based dosing of growth hormone therapy in children: a randomized, controlled study. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2007;92(7):2480‐6. [0021‐972X] - PubMed
Collins 2004 {published data only}
-
- Collins CD, Pedersen CA, Schneider PJ, Miller AS, Sierawski SJ, Roux RK. Effect on amphotericin B lipid complex use of a clinical decision support system for computerized prescriber order entry. American Journal of Health‐System Pharmacy 2004;61(13):1395‐9. [1079‐2082] - PubMed
Cupissol 1996 {published data only}
-
- Cupissol D, BrŠS J, Gestin‐Boyer C, Nouguier‐Soul‚ J, Vian L, Tep A, et al. Validation of a new interactive software monitoring a controlled‐flow infusion pump for cisplatin dosage regimen adjustment. Bulletin du Cancer 1996;83(8):664‐76. - PubMed
Demakis 2000 {published data only}
-
- Demakis JG, Beauchamp C, Cull WL, Denwood R, Eisen SA, Lofgren R, et al. Improving residents' compliance with standards of ambulatory care. Results from the VA Cooperative Study on Computerized Reminders. JAMA 2000;284:1411‐6. - PubMed
Dillon 1989 {published data only}
-
- Dillon KR, Dougherty SH, Casner P, Polly S. Individualized pharmacokinetic versus standard dosing of amikacin: a comparison of therapeutic outcomes. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1989;24:581‐9. - PubMed
Donovan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Donovan JL, Kanaan AO, Thomson MS, Rochon P, Lee M, Gavendo L, et al. Effect of clinical decision support on psychotropic medication prescribing in the long‐term care setting. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2010;58(5):1005‐7. [0002‐8614] - PubMed
Doran 2004 {published data only}
-
- Doran CV, Hudson NH, Moorhead KT, Chase JG, Shaw GM, Hann CE. Derivative weighted active insulin control modelling and clinical trials for ICU patients. Medical Engineering & Physics 2004; Vol. 26, issue 10:855‐66. [1350‐4533] - PubMed
Dortch 2008 {published data only}
-
- Dortch MJ, Mowery NT, Ozdas A, Dossett L, Cao H, Collier B, et al. A computerized insulin infusion titration protocol improves glucose control with less hypoglycemia compared to a manual titration protocol in a trauma intensive care unit. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2008;32(1):18‐27. [0148‐6071] - PubMed
Evans 1998 {published data only}
-
- Evans RS, Pestotnik SL, Classen DC, Clemmer TP, Weaver LK, Orme JF, et al. A computer‐assisted management program for antibiotics and other antiinfective agents. New England Journal of Medicine 1998;338(4):232‐8. [0028‐4793] - PubMed
Evans 1998a {published data only}
-
- Evans WE, Relling MV, Rodman JH, Crom WR, Boyett JM, Pui CH. Conventional compared with individualized chemotherapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. New England Journal of Medicine 1998;338(8):499‐505. [0028‐4793] - PubMed
Evans 1999 {published data only}
-
- Evans RS, Pestotnik SL, Classen DC, Burke JP. Evaluation of a computer‐assisted antibiotic‐dose monitor. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 1999;33(10):1026‐31. [1060‐0280] - PubMed
Faber 2006 {published data only}
-
- Faber E, Pytlik R, Slaby J, Zapletalova J, Kozak T, Raida L, et al. Individually determined dosing of filgrastim after autologous peripheral stem cell transplantation in patients with malignant lymphoma ‐ results of a prospective multicentre controlled trial. European Journal of Haematology 2006;77(6):493‐500. [0902‐4441] - PubMed
Feldstein 2006 {published data only}
-
- Feldstein AC, Smith DH, Perrin N, Yang X, Rix M, Raebel MA, et al. Improved therapeutic monitoring with several interventions. A randomized trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2006;166:1848‐54. - PubMed
Fety 1998 {published data only}
-
- Fety R, Rolland F, Barberi‐Heyob M, Hardouin A, Campion L, Conroy T, et al. Clinical impact of pharmacokinetically‐guided dose adaptation of 5‐fluorouracil: results from a multicentric randomized trial in patients with locally advanced head and neck carcinomas. Clinical Cancer Research 1998;4(9):2039‐45. [1078‐0432] - PubMed
Field 2009 {published data only}
Field 2009a {published data only}
Fihn 1994 {published data only}
-
- Fihn SD, McDonell MB, Vermes D, Henikoff JG, Martin DC, Callahan CM, et al. A computerized intervention to improve timing of outpatient follow‐up: a multicenter randomized trial in patients treated with warfarin. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1994;9(3):131‐9. - PubMed
Fitzmaurice 1996 {published data only}
Fitzmaurice 1998 {published data only}
-
- Fitzmaurice DA, Hobbs FD, Murray ET. Primary care anticoagulant clinic management using computerized decision support and near patient international normalized ratio (INR) testing: routine data from a practice nurse‐led clinic. Family Practice 1998;15(2):144‐6. - PubMed
Flanders 2009 {published data only}
-
- Flanders SJ, Juneja R, Roudebush CP, Carroll J, Golas A, Elias BL. Glycemic control and insulin safety: the impact of computerized intravenous insulin dosing. American Journal of Medical Quality 2009; Vol. 24, issue 6:489‐97. - PubMed
Fritsch 2009 {published data only}
-
- Fritsch N, Nouette‐Gaulain K, Bordes M, Semjen F, Meymat Y, Cros A‐M. Target‐controlled inhalation induction with sevoflurane in children: a prospective pilot study. Paediatric Anaesthesia 2009;19(2):126‐32. - PubMed
Fukudo 2009 {published data only}
-
- Fukudo M, Yano I, Shinsako K, Katsura T, Takada Y, Uemoto S, et al. Prospective evaluation of the Bayesian method for individualizing tacrolimus dose early after living‐donor liver transplantation. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2009;49(7):789‐97. [0091‐2700] - PubMed
Gamelin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Gamelin E, Delva R, Jacob J, Merrouche Y, Raoul JL, Pezet D, et al. Individual fluorouracil dose adjustment based on pharmacokinetic follow‐up compared with conventional dosage: results of a multicenter randomized trial of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2008;26(13):2099‐105. - PubMed
Ghazal‐Aswad 1997 {published data only}
-
- Ghazal‐Aswad S, Highley M, Bailey N, Lind M, Siddiqui N, Sinha DP, et al. A randomised phase III study to compare the toxicity and efficacy of carboplatin given by pharmacokinetically guided formula compared to conventional dosing in epithelial ovarian cancer. Acta Obstetrica et Gynecologica Scandinavica 1997;76:26.
Gopakumaran 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gopakumaran B. "Intelligent dosing system": a useful computer program for diabetes management?. Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics 2004; Vol. 6, issue 3:336‐8. [1520‐9156] - PubMed
Griffey 2012 {published data only}
Guarracino 2001 {published data only}
-
- Guarracino F, Cosmo D, Penzo D, Tedesco M, Bossi A, Zussa C, et al. Automated protamine dose assay in heparin reversal management after cardiopulmonary by pass. Minerva Anestesiologica 2001;67(4):165‐9. [0375‐9393] - PubMed
Guarracino 2003 {published data only}
-
- Guarracino F, Penzo D, Cosmo D, Vardanega A, Stefani R. Pharmacokinetic‐based total intravenous anaesthesia using remifentanil and propofol for surgical myocardial revascularization. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2003;20(5):385‐90. [0265‐0215] - PubMed
Hermayer 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hermayer KL, Neal DE, Hushion TV, Irving MG, Arnold PC, Kozlowski L, et al. Outcomes of a cardiothoracic intensive care web‐based online intravenous insulin infusion calculator study at a Medical University Hospital. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics 2007;9(6):523‐34. [1520‐9156] - PubMed
Hobbs 1996 {published data only}
-
- Hobbs FD, Delaney BC, Carson A, Kenkre JE. A prospective controlled trial of computerized decision support for lipid management in primary care. Family Practice 1996;13(2):133‐7. - PubMed
Hoffman 2004 {published data only}
-
- Hoffman AR, Strasburger CJ, Zagar A, Blum WF, Kehely A, Hartman ML, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of an individualized dosing regimen for adult growth hormone replacement therapy in comparison with fixed body weight‐based dosing. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2004;89(7):3224‐33. [0021‐972X] - PubMed
Horn 2002 {published data only}
-
- Horn W, Popow C, Miksch S, Kirchner L, Seyfang A. Development and evaluation of VIE‐PNN, a knowledge‐based system for calculating the parenteral nutrition of newborn infants. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 2002;24(3):217‐28. - PubMed
Hwang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Hwang HG, Chang IC, Hung WF, Sung ML, Yen D. The design and evaluation of clinical decision support systems in the area of pharmacokinetics. Medical Informatics and the Internet in Medicine 2004;29(3‐4):239‐51. - PubMed
Jankovic 1999 {published data only}
-
- Jankovic SM, Timotijevic I, Mihajlovic GS, Dukic‐Dejanovic S. Comparison of two approaches to amitriptyline dose individualisation. European Journal of Drug Metabolism & Pharmacokinetics 1999;24(2):163‐8. [0398‐7639] - PubMed
Jannuzzi 2000 {published data only}
-
- Jannuzzi G, Cian P, Fattore C, Gatti G, Bartoli A, Monaco F, et al. A multicenter randomized controlled trial on the clinical impact of therapeutic drug monitoring in patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy. The Italian TDM Study Group in Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2000;41(2):222‐30. [0013‐9580] - PubMed
Jellinek 2005 {published data only}
-
- Jellinek SP, Cohen V, Likourezos A, Goldman WM, Lashley EL. Analyzing a health‐system's use of unfractionated heparin to ensure optimal anticoagulation. Journal of Pharmacy Technology 2005;21(2):69‐78. [8755‐1225]
Judge 2006 {published data only}
Jung 2009 {published data only}
-
- Jung H, Land C, Nicolay C, Schepper J, Blum WF, Schonau E. Growth response to an individualized versus fixed dose GH treatment in short children born small for gestational age: the OPTIMA study. European Journal of Endocrinology 2009; Vol. 160, issue 2:149‐56. - PubMed
Kazemi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kazemi A, Ellenius J, Pourasghar F, Tofighi S, Salehi A, Amanati A, et al. The effect of computerized physician order entry and decision support system on medication errors in the neonatal ward: e xperiences from an Iranian teaching hospital. Journal of Medical Systems 2011;35(1):25‐37. [0148‐5598] - PubMed
Kirk 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kirk RC, Li‐Meng Goh D, Packia J, Min Kam H, Ong BKC. Computer calculated dose in paediatric prescribing. Drug Safety 2005;28(9):817‐24. [0114‐5916] - PubMed
Koide 2000 {published data only}
-
- Koide D, Ohe K, Ross‐Degnan D, Kaihara S. Computerized reminders to monitor liver function to improve the use of etretinate. International Journal of Medical Informatics 2000;57:11‐9. - PubMed
Kristrom 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kristrom B, Aronson AS, Dahlgren J, Gustafsson J, Halldin M, Ivarsson SA, et al. Growth hormone (GH) dosing during catch‐up growth guided by individual responsiveness decreases growth response variability in prepubertal children with GH deficiency or idiopathic short stature. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2009;94(2):483‐90. [0021‐972X] - PubMed
Kroese 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kroese WLG, Avery AJ, Savelyich BSP, Brown NS, Schers H, Howard R, et al. Assessing the accuracy of a computerized decision support system for digoxin dosing in primary care: an observational study. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy & Therapeutics 2005;30(3):279‐83. [0269‐4727] - PubMed
la Cour Freiesleben 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cour Freiesleben N, Lossl K, Bogstad J, Bredkjaer HE, Toft B, Rosendahl M, et al. Individual versus standard dose of rFSH in a mild stimulation protocol for intrauterine insemination: a randomized study. Human Reproduction 2009;24(10):2523‐30. - PubMed
Lester 2006 {published data only}
Ligtenberg 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ligtenberg JJ, Meertens JH, Monteban‐Kooistra WE, Tulleken JE, Zijlstra JG. Multicentric, randomized, controlled trial to evaluate blood glucose control by the model predictive control algorithm versus routine glucose management protocols in intensive care unit patients: response to Plank et al. Diabetes Care 2006; Vol. 29, issue 8:1987‐8. - PubMed
Lillis 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lillis K. Automated dosing. Computerized physician order entry reduces risk of medication and dosing errors in neonatal ICU. Health Management Technology 2003;24(11):36‐7. [1074‐4770] - PubMed
Liu 2006 {published data only}
-
- Liu N, Chazot T, Genty A, Landais A, Restoux A, McGee K, et al. Titration of propofol for anesthetic induction and maintenance guided by the bispectral index: closed‐loop versus manual control. A prospective, randomized, multicenter study. Anesthesiology 2006;104(4):686‐95. [0003‐3022] - PubMed
Manotti 2001 maintenance {published data only}
-
- Manotti C, Moia M, Palareti G, Pengo V, Ria L, Dettori AG. Effect of computer‐aided management on the quality of treatment in anticoagulated patients: a prospective, randomized, multicenter trial of APROAT (Automated PRogram for Oral Anticoagulant Treatment). Haematologica 2001;86(10):1060‐70. - PubMed
Mar Fernandez 1996 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez de Gatta MD, Calvo MV, Hernandez JM, Caballero D, San Miguel JF, Dominguez‐Gil A. Cost‐effectiveness analysis of serum vancomycin concentration monitoring in patients with hematologic malignancies. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics 1996;60(3):332‐40. [0009‐9236] - PubMed
Mar Fernandez 2009 {published data only}
-
- Mar Fernandez de Gatta MD, Victoria Calvo M, Ardanuy R, Dominguez‐Gil A, Lanao JM, Moreno SR. Evaluation of population pharmacokinetic models for amikacin dosage individualization in critically ill patients. Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmacology 2009;61(6):759‐66. [0022‐3573] - PubMed
Matheny 2008 {published data only}
Maurizi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Maurizi AR, Lauria A, Maggi D, Palermo A, Fioriti E, Manfrini S, et al. A novel insulin unit calculator for the management of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics 2011;13:425‐8. - PubMed
McCluggage 2010 {published data only}
-
- McCluggage L, Lee K, Potter T, Dugger R, Pakyz A. Implementation and evaluation of vancomycin nomogram guidelines in a computerized prescriber‐order‐entry system. American Journal of Health‐System Pharmacy 2010;67(1):70‐5. - PubMed
McCowan 2001 {published data only}
-
- McCowan C, Neville RG, Ricketts IW, Warner FC, Hoskins G, Thomas GE. Lessons from a randomized controlled trial designed to evaluate computer decision support software to improve the management of asthma. Medical Informatics and the Internet in Medicine 2001;26:191‐201. - PubMed
McCoy 2008 {published data only}
-
- McCoy AB, Peterson JF, Gadd CS, Danciu I, Waitman LR. A system to improve medication safety in the setting of acute kidney injury: initial provider response. Annual Symposium Proceedings/AMIA Symposium 2008:1051. - PubMed
McCoy 2010 {published data only}
McDonald 1976 {published data only}
-
- McDonald CJ. Use of a computer to detect and respond to clinical events: its effect on clinician behavior. Annals of Internal Medicine 1976;84(2):162‐7. - PubMed
McDonald 1980 {published data only}
-
- McDonald CJ, Wilson GA, McCabe GP, Jr. Physician response to computer reminders. JAMA 1980;244(14):1579‐81. - PubMed
McMichael 1993 {published data only}
McMullin 1997 {published data only}
-
- McMullin ST, Reichley RM, Kahn MG, Dunagan WC, Bailey TC. Automated system for identifying potential dosage problems at a large university hospital. American Journal of Health‐System Pharmacy 1997;54(5):545‐9. [1079‐2082] - PubMed
McMullin 2004 {published data only}
McMullin 2005 {published data only}
Motykie 1999 {published data only}
-
- Motykie GD, Mokhtee D, Zebala LP, Caprini JA, Kudrna JC, Mungall DR. The use of a Bayesian forecasting model in the management of warfarin therapy after total hip arthroplasty. Journal of Arthroplasty 1999;14(8):988‐93. [0883‐5403] - PubMed
Mullett 2001 {published data only}
-
- Mullett CJ, Evans RS, Christenson JC, Dean JM. Development and impact of a computerized pediatric antiinfective decision support program. Pediatrics 2001;108(4):E75. - PubMed
Murchie 1989 {published data only}
-
- Murchie CJ, Kenny GN. Comparison among manual, computer‐assisted, and closed‐loop control of blood pressure after cardiac surgery. Journal of Cardiothoracic Anesthesia 1989;3(1):16‐19. - PubMed
Nash 2005 {published data only}
-
- Nash IS, Rojas M, Hebert P, Marrone SR, Colgan C, Fisher LA, et al. Reducing excessive medication administration in hospitalized adults with renal dysfunction. American Journal of Medical Quality 2005;20(2):64‐9. [1062‐8606] - PubMed
Newby 2002 {published data only}
-
- Newby LK, Harrington RA, Bhapkar MV, Werf F, Hochman JS, Granger CB, et al. An automated strategy for bedside aPTT determination and unfractionated heparin infusion adjustment in acute coronary syndromes: insights from PARAGON A. Journal of Thrombosis & Thrombolysis 2002;14(1):33‐42. [0929‐5305] - PubMed
Nieuwenhuyze 1995 {published data only}
-
- Nieuwenhuyzen MC, Engbers FH, Burm AG, Vletter AA, Kleef JW, Bovill JG. Computer‐controlled infusion of alfentanil versus patient‐controlled administration of morphine for postoperative analgesia: a double‐blind randomized trial. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1995;81(4):671‐9. - PubMed
Nightingale 2000 {published data only}
Oppenheim 2002 {published data only}
Overhage 1997 {published data only}
Palen 2006 {published data only}
-
- Palen TE, Raebel M, Lyons E, Magid DM. Evaluation of laboratory monitoring alerts within a computerized physician order entry system for medication orders. American Journal of Managed Care 2006;12:389‐95. - PubMed
Pea 2002 {published data only}
-
- Pea F, Bertolissi M, Silvestre A, Poz D, Giordano F, Furlanut M. TDM coupled with Bayesian forecasting should be considered an invaluable tool for optimizing vancomycin daily exposure in unstable critically ill patients. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2002;20(5):326‐32. [0924‐8579] - PubMed
Peck 1973 {published data only}
-
- Peck CC, Sheiner LB, Martin CM, Combs DT, Melmon KL. Computer‐assisted digoxin therapy. New England Journal of Medicine 1973;289(9):441‐6. - PubMed
Peters 1996 {published data only}
-
- Peters A, Kerner W. Analytical design and clinical application of an intelligent control system for insulin treatment [Analytisches Design und klinische Anwendung eineslernfähigen Regelsystems für die Pharmakotherapie mit Insulin]. Biomedizinische Technik 1996;41(1‐2):2‐13. - PubMed
Peterson 1986 {published data only}
-
- Peterson CM, Jovanovic L, Chanoch LH. Randomized trial of computer‐assisted insulin delivery in patients with type I diabetes beginning pump therapy. American Journal of Medicine 1986;81(1):69‐72. - PubMed
Peterson 2005 {published data only}
-
- Peterson JF, Kuperman GJ, Shek C, Patel M, Avorn J, Bates DW. Guided prescription of psychotropic medications for geriatric inpatients. Archives of Internal Medicine 2005;165(7):802‐7. [0003‐9926] - PubMed
Peterson 2007 {published data only}
-
- Peterson JF, Rosenbaum BP, Waitman LR, Habermann R, Powers J, Harrell D, et al. Physicians' response to guided geriatric dosing: initial results from a randomized trial. Studies in Health Technology & Informatics 2007;129(Pt 2):1037‐40. [0926‐9630] - PubMed
Phillips 2008 {published data only}
-
- Phillips IE, Nelsen C, Peterson J, Sullivan TM, Waitman LR. Improving aminoglycoside dosing through computerized clinical decision support and pharmacy therapeutic monitoring systems. AMIA 2008; Vol. Annual Symposium Proceedings/AMIA Symposium.:1093. - PubMed
Piazza 2009 {published data only}
Poller 1993 {published data only}
Popovic‐Todorovic 2003 {published data only}
-
- Popovic‐Todorovic B, Loft A, Bredkjaeer HE, Bangsboll S, Nielsen IK, Andersen AN. A prospective randomized clinical trial comparing an individual dose of recombinant FSH based on predictive factors versus a 'standard' dose of 150 IU/day in 'standard' patients undergoing IVF/ICSI treatment. Human Reproduction 2003;18(11):2275‐82. [0268‐1161] - PubMed
Proost 2003 {published data only}
-
- Proost JH, Punt NC. Dose individualization in PharmDIS‐e+. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2003;41(10):451‐8. [0946‐1965] - PubMed
Roberts 2010 {published data only}
-
- Roberts GW, Farmer CJ, Cheney PC, Govis SM, Belcher TW, Walsh SA, et al. Clinical decision support implemented with academic detailing improves prescribing of key renally cleared drugs in the hospital setting. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2010; Vol. 17, issue 3:308‐12. - PMC - PubMed
Rochon 2006 {published data only}
Rood 2005 {published data only}
Rothschild 2002 {published data only}
Rothschild 2003 {published data only}
Rothschild 2005 {published data only}
-
- Rothschild JM, Keohane CA, Cook EF, Orav EJ, Burdick E, Thompson S, et al. A controlled trial of smart infusion pumps to improve medication safety in critically ill patients. Critical Care Medicine 2005; Vol. 33, issue 3:533‐40. [0090‐3493] - PubMed
Rotman 1996 {published data only}
-
- Rotman BL, Sullivan AN, McDonald TW, Brown BW, DeSmedt P, Goodnature D, et al. A randomized controlled trial of a computer based physician workstation in an outpatient setting: implementation barriers to outcome evaluation. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 1996;3(5):340‐8. - PMC - PubMed
Roumie 2005 {published data only}
-
- Roumie CL, Elasy TA, Greevy R, Griffin MR, Liu X, Stone WJ, et al. Improving blood pressure control through provider education, provider alerts, and patient education: a cluster randomized trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 2006;145:165‐75. - PubMed
Ruiz 1993 {published data only}
-
- Ruiz R, Borches D, Gonzalez A, Corral J. A new sodium‐nitroprusside‐infusion controller for the regulation of arterial blood pressure. Biomedical Instrumentation & Technology 1993;27(3):244‐51. - PubMed
Ryff‐de Leche 1992 {published data only}
-
- Ryff‐de Leche A, Engler H, Nutzi E, Berger M, Berger W. Clinical application of two computerized diabetes management systems: comparison with the log‐book method. Diabetes Research 1992;19(3):97‐105. - PubMed
Santana 2003 {published data only}
-
- Santana VM, Zamboni WC, Kirstein MN, Tan M, Liu T, Gajjar A, et al. A pilot study of protracted topotecan dosing using a pharmacokinetically guided dosing approach in children with solid tumors. Clinical Cancer Research 2003;9(2):633‐40. [1078‐0432] - PubMed
Santana 2005 {published data only}
-
- Santana VM, Furman WL, Billups CA, Hoffer F, Davidoff AM, Houghton PJ, et al. Improved response in high‐risk neuroblastoma with protracted topotecan administration using a pharmacokinetically guided dosing approach. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2005; Vol. 23, issue 18:4039‐47. [0732‐183X] - PubMed
Schneider 2005 {published data only}
-
- Schneider BL, Gulseth MP, Cusick MA, Sisson DC, Tomsche JJ. Computer program to assist pharmacy management of an inpatient warfarin dosing service. American Journal of Health‐System Pharmacy 2005;62(22):2393‐6. [1079‐2082] - PubMed
Schrezenmeir 2002 {published data only}
-
- Schrezenmeir J, Dirting K, Papazov P. Controlled multicenter study on the effect of computer assistance in intensive insulin therapy of type 1 diabetics. Computer Methods & Programs in Biomedicine 2002;69(2):97‐114. [0169‐2607] - PubMed
Shiach 2002 {published data only}
-
- Shiach CR, Campbell B, Poller L, Keown M, Chauhan N. Randomised cross‐over study of near patient testing versus hospital laboratory testing with computer assisted dosing in a community anticoagulant clinic. British Journal of Haematology 2002;117(Suppl 1):33. - PubMed
Shieh 2006 {published data only}
-
- Shieh J‐S, Fu M, Huang S‐J, Kao M‐C. Comparison of the applicability of rule‐based and self‐organizing fuzzy logic controllers for sedation control of intracranial pressure pattern in a neurosurgical intensive care unit. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2006;53(8):1700‐5. [0018‐9294] - PubMed
Soper 2006 {published data only}
-
- Soper J, Chan GTC, Skinner JR, Spinetto HD, Gentles TL. Management of oral anticoagulation in a population of children with cardiac disease using a computerised system to support decision‐making. Cardiology in the Young 2006;16(3):256‐60. [1047‐9511] - PubMed
Sparano 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sparano JA. TAILORx: trial assigning individualized options for treatment (Rx). Clinical Breast Cancer 2006;7(4):347‐50. [1526‐8209] - PubMed
Strack 1985 {published data only}
-
- Strack T, Bergeler J, Beyer J, Hutten H. Computer assisted conventional insulin therapy. Life Support Systems 1985;3 Suppl 1:568‐72. - PubMed
Tamblyn 2003 {published data only}
Tamblyn 2008 {published data only}
Tamblyn 2010 {published data only}
-
- Tamblyn R, Reidel K, Huang A, Taylor L, Winslade N, Bartlett G, et al. Increasing the detection and response to adherence problems with cardiovascular medication in primary care through computerized drug management systems: a randomized controlled trial. Medical Decision Making 2010;30(2):176‐88. - PubMed
Terrell 2009 {published data only}
-
- Terrell KM, Perkins AJ, Dexter PR, Hui SL, Callahan CM, Miller DK. Computerized decision support to reduce potentially inappropriate prescribing to older emergency department patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2009;57(8):1388‐94. - PubMed
Thomson 2011 {published data only}
Tierney 2005 {published data only}
-
- Tierney WM, Overhage JM, Murray MD, Harris LE, Zhou XH, Eckert GJ, et al. Can computer‐generated evidence‐based care suggestions enhance evidence‐based management of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? A randomized, controlled trial. Health Services Research 2005;40:477‐97. - PMC - PubMed
Tomek 2011 {published data only}
-
- Tomek A, Mat'oka V, Kumstov T, Rmek M, Arbochov I, T'ovkov K, et al. Warfarin loading dose guided by pharmacogenetics is effective and safe in cardioembolic stroke patients. Proceedings of the 20th European Stroke Conference; 2011 May 24‐27; Hamburg, Germany. 2011.
Traugott 2011 {published data only}
-
- Traugott KA, Maxwell PR, Green K, Frei C, Lewis JS, 2nd. Effects of therapeutic drug monitoring criteria in a computerized prescriber‐order‐entry system on the appropriateness of vancomycin level orders. American Journal of Health‐System Pharmacy 2011;68(4):347‐52. - PubMed
Trivedi 2007 {published data only}
Trivedi 2007a {published data only}
-
- Trivedi MH, Rush AJ, Gaynes BN, Stewart JW, Wisniewski SR, Warden D, et al. Maximizing the adequacy of medication treatment in controlled trials and clinical practice: STAR(*)D measurement‐based care. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007;32(12):2479‐89. [0893‐133X] - PubMed
van der Bol 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bol JM, Mathijssen RHJ, Creemers G‐JM, Planting AST, Loos WJ, Wiemer EAC, et al. A CYP3A4 phenotype‐based dosing algorithm for individualized treatment of irinotecan. Clinical Cancer Research 2010;16(2):736‐42. [1078‐0432] - PubMed
van Leeuwen 2005 {published data only}
-
- Leeuwen Y, Rombouts EK, Kruithof CJ, Meer FJM, Rosendaal FR. Comparison between two computer algorithms in oral anticoagulant dosage: a double blind randomised controlled trial. Journal of Thrombosis & Haemostasis 2005; Vol. 3:1.
van Leeuwen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Leeuwen Y, Rombouts EK, Kruithof CJ, Meer FJM, Rosendaal FR. Improved control of oral anticoagulant dosing: a randomized controlled trial comparing two computer algorithms. Journal of Thrombosis & Haemostasis 2007;5(8):1644‐9. [1538‐7933] - PubMed
van Lent‐Evers 1999 {published data only}
-
- Lent‐Evers NA, Mathot RA, Geus WP, Hout BA, Vinks AA. Impact of goal‐oriented and model‐based clinical pharmacokinetic dosing of aminoglycosides on clinical outcome: a cost‐effectiveness analysis. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 1999;21(1):63‐73. [0163‐4356] - PubMed
Van Wyk 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wyk JT, Wijk MAM, Sturkenboom MCJM, Mosseveld M, Moorman PW, Lei J. Electronic alerts versus on‐demand decision support to improve dyslipidemia treatment: a cluster randomized controlled trial. Circulation 2008; Vol. 117, issue 3:371‐8. [0009‐7322] - PubMed
Verstappen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Verstappen SMM, Jacobs JWG, Veen MJ, Heurkens AHM, Schenk Y, ter Borg EJ, et al. Intensive treatment with methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis: aiming for remission. Computer Assisted Management in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis (CAMERA, an open‐label strategy trial). Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2007;66(11):1443‐9. [0003‐4967] - PMC - PubMed
Verstappen 2010 {published data only}
-
- Verstappen SMM, Bakker MF, Heurkens AHM, Veen MJ, Kruize AA, Geurts MAW, et al. Adverse events and factors associated with toxicity in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis treated with methotrexate tight control therapy: the CAMERA study. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2010; Vol. 69, issue 6:1044‐8. - PubMed
Wasmuth 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wasmuth JC, Lambertz I, Voigt E, Vogel M, Hoffmann C, Burger D, et al. Maintenance of indinavir by dose adjustment in HIV‐1‐infected patients with indinavir‐related toxicity. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2007;63(10):901‐8. - PubMed
Wasmuth 2007a {published data only}
-
- Wasmuth JC, Rodermann E, Voigt E, Vogel M, Lauenroth‐Mai E, Jessen A, et al. Comparison of indinavir + ritonavir 600 + 100 mg vs. 400 + 100 mg BID combinations in HIV1‐infected patients guided by therapeutic drug monitoring. European Journal of Medical Research 2007;12(7):289‐94. [0949‐2321] - PubMed
Whipple 1991 {published data only}
-
- Whipple JK, Ausman RK, Franson T, Quebbeman EJ. Effect of individualized pharmacokinetic dosing on patient outcome. Critical Care Medicine 1991;19:1480‐5. - PubMed
White 1984 {published data only}
-
- White KS, Lindsay A, Pryor TA, Brown WF, Walsh K. Application of a computerized medical decision‐making process to the problem of digoxin intoxication. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 1984;4(3):571‐6. - PubMed
Willcourt 1994 {published data only}
-
- Willcourt RJ, Pager D, Wendel J, Hale RW. Induction of labor with pulsatile oxytocin by a computer‐controlled pump. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1994;170(2):603‐8. - PubMed
Wilson 2002 {published data only}
-
- Wilson WH, Grossbard ML, Pittaluga S, Cole D, Pearson D, Drbohlav N, et al. Dose‐adjusted EPOCH chemotherapy for untreated large B‐cell lymphomas: a pharmacodynamic approach with high efficacy. Blood 2002;99(8):2685‐93. [0006‐4971] - PubMed
Yamamoto 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yamamoto N, Tamura T, Murakami H, Shimoyama T, Nokihara H, Ueda Y, et al. Randomized pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of docetaxel: dosing based on body‐surface area compared with individualized dosing based on cytochrome P450 activity estimated using a urinary metabolite of exogenous cortisol. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2005;23(6):1061‐9. [0732‐183X] - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Anderson 2011 {published data only}
-
- Anderson JL, Horne BD, Stevens SM, Woller SC, Samuelson KM, Mansfield JW, et al. A randomized and clinical effectiveness trial comparing two pharmacogenetic algorithms and standard care for individualizing warfarin dosing: CoumaGen‐II. Proceedings of the American Heart Association; 2011 Nov 12‐16; Orlando, FL. 2011. - PubMed
Anderson 2012 {published data only}
-
- Anderson JL, Horne BD, Stevens SM, Woller SC, Samuelson KM, Mansfield JW, et al. A randomized and clinical effectiveness trial comparing two pharmacogenetic algorithms and standard care for individualizing warfarin dosing (CoumaGen‐II). Circulation 2012;125(16):1997‐2005. [PUBMED: 22431865] - PubMed
Caduff 2013 {published data only}
-
- Caduff Good A, Nobel D, Krahenbuhl S, Geisen C, Henz S. Randomised trial of a clinical dosing algorithm to start anticoagulation with phenprocoumon. Swiss Medical Weekly 2013;143:w13709. [PUBMED: 23299853] - PubMed
Dumont 2012 {published data only}
-
- Dumont C, Bourguignon C. Effect of a computerized insulin dose calculator on the process of glycemic control. American Journal of Critical Care 2012;21(2):106‐15. [PUBMED: 22381987] - PubMed
Horibe 2012 {published data only}
-
- Horibe M, Nair BG, Yurina G, Neradilek MB, Rozet I. A novel computerized fading memory algorithm for glycemic control in postoperative surgical patients. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2012;115(3):580‐7. [PUBMED: 22669346] - PubMed
Jeanne 2012 {published data only}
-
- Jeanne M, Clement C, Jonckheere J, Logier R, Tavernier B. Variations of the analgesia nociception index during general anaesthesia for laparoscopic abdominal surgery. Journal of Clinical Monitoring and Computing 2012;26(4):289‐94. [PUBMED: 22454275] - PubMed
Joerger 2012 {published data only}
-
- Joerger M, Kraff S, Huitema AD, Feiss G, Moritz B, Schellens JH, et al. Evaluation of a pharmacology‐driven dosing algorithm of 3‐weekly paclitaxel using therapeutic drug monitoring: a pharmacokinetic‐pharmacodynamic simulation study. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 2012;51(9):607‐17. [PUBMED: 22804749] - PubMed
Kelly 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kelly PJ, Kay‐Lambkin FJ, Baker AL, Deane FP, Brooks AC, Mitchell A, et al. Study protocol: a randomized controlled trial of a computer‐based depression and substance abuse intervention for people attending residential substance abuse treatment. BMC Public Health 2012;12:113. [PUBMED: 22325594] - PMC - PubMed
Kim 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kim S, Lee HW, Lee W, Um TH, Cho CR, Chun S, et al. New allele‐specific real‐time PCR system for warfarin dose genotyping equipped with an automatic interpretative function that allows rapid, accurate, and user‐friendly reporting in clinical laboratories. Thrombosis Research 2012;130(1):104‐9. [PUBMED: 21911247] - PubMed
Magee 2012 {published data only}
Nieuwlaat 2011 {published data only}
-
- Nieuwlaat R, Spyropoulos AC, Hubers L, Stehouwer A, Spall HG, Eikelboom JW, et al. Randomized comparison of the DAWN AC computer program and a simple manual nomogram for quality of warfarin dosing. 23rd Congress of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 2011; Vol. Proceedings of the 57th Annual SSC Meeting; 2011 Jul 23‐28; Kyoto Japan;:302.
Nieuwlaat 2012 {published data only}
-
- Nieuwlaat R, Hubers LM, Spyropoulos AC, Eikelboom JW, Connolly BJ, Spall HG, et al. Randomised comparison of a simple warfarin dosing algorithm versus a computerised anticoagulation management system for control of warfarin maintenance therapy. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 2012;108(6):1228‐35. [PUBMED: 23015161] - PubMed
Overgaard 2010 {published data only}
-
- Overgaard K, Corell P, Madsen P, Rasmussen RS. Computer‐aid improves oral anticoagulant therapy. Proceedings of the 19th European Stroke Conference; 2010 May 25‐28; Barcelona, Spain. 2010.
Pielmeier 2012 {published data only}
-
- Pielmeier U, Rousing ML, Andreassen S, Nielsen BS, Haure P. Decision support for optimized blood glucose control and nutrition in a neurotrauma intensive care unit: preliminary results of clinical advice and prediction accuracy of the Glucosafe system. Journal of Clinical Monitoring and Computing 2012;26(4):319‐28. [PUBMED: 22581038] - PubMed
Radhakrishnan 2012 {published data only}
-
- Radhakrishnan A, Vido D, Tayur S, Akan M, Murali S. Genotype guided therapeutic dosing of warfarin in geriatric patients. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2012;59(13 Suppl 1):E1696.
Rasmussen 2012 {published data only}
Spaniel 2012 {published data only}
-
- Spaniel F, Hrdlicka J, Novak T, Kozeny J, Hoschl C, Mohr P, et al. Effectiveness of the information technology‐aided program of relapse prevention in schizophrenia (ITAREPS): a randomized, controlled, double‐blind study. Journal of Psychiatric Practice 2012;18(4):269‐80. [PUBMED: 22805901] - PubMed
Tamblyn 2012 {published data only}
-
- Tamblyn R, Eguale T, Buckeridge DL, Huang A, Hanley J, Reidel K, et al. The effectiveness of a new generation of computerized drug alerts in reducing the risk of injury from drug side effects: a cluster randomized trial. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2012;19(4):635‐43. [PUBMED: 22246963] - PMC - PubMed
Whitehead 2012 {published data only}
-
- Whitehead J, Thygesen H, Jaki T, Davies S, Halford S, Turner H, et al. A novel phase I/IIa design for early phase oncology studies and its application in the evaluation of MK‐0752 in pancreatic cancer. Statistics in Medicine 2012;31(18):1931‐43. [PUBMED: 22495759] - PubMed
Wiltshire 2012 {published data only}
-
- Wiltshire HR, Kilpatrick GJ, Tilbrook GS, Borkett KM. A placebo‐ and midazolam‐controlled phase I single ascending‐dose study evaluating the safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of remimazolam (CNS 7056): Part II. Population pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling and simulation. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2012;115(2):284‐96. [PUBMED: 22253270] - PubMed
Additional references
Arditi 2012
-
- Arditi C, Rège‐Walther M, Wyatt JC, Durieux P, Burnand B. Computer‐generated reminders delivered on paper to healthcare professionals; effects on professional practice and health care outcomes. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 12. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001175.pub3] - DOI - PubMed
Baldwin 1995
Bates 2003
Brennan 1991
-
- Brennan TA, Leape LL, Laird NM, Hebert L, Localio AR, Lawthers AG, et al. Incidence of adverse events and negligence in hospitalized patients. Results of the Harvard Medical Practice Study I. New England Journal of Medicine 1991;324(6):370‐6. - PubMed
Chatellier 1998
-
- Chatellier G, Colombet I, Degoulet P. Computer‐adjusted dosage of anticoagulant therapy improves the quality of anticoagulation. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics 1998;52(Pt 2):819‐23. - PubMed
CLINICIP
-
- CLINICIP Project. CLINICIP (Closed Loop Insulin Infusion for Critically Ill Patients). www.clinicip.org (accessed 25 September 2013).
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Durieux 2005
-
- Durieux P. Electronic medical alerts ‐ so simple, so complex. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;352(10):1034‐6. - PubMed
EPOC 2009
-
- EPOC. Risk of bias ‐ EPOC specific. epoc.cochrane.org/sites/epoc.cochrane.org/files/uploads/Risk%20of%20Bias... (accessed 25 September 2013).
EPOC 2012
-
- EPOC. What study designs should be included in an EPOC review and what should they be called?. epocoslo.cochrane.org/sites/epocoslo.cochrane.org/files/uploads/What%20s... (accessed 25 September 2013).
Eslami 2009
Fitzmaurice 1998a
-
- Fitzmaurice DA, Hobbs FD, Delaney BC, Wilson S, McManus R. Review of computerized decision support systems for oral anticoagulation management. British Journal of Haematology 1998;102(4):907‐9. - PubMed
Franke 2000
-
- Franke L, Avery AJ, Groom L, Horsfield P. Is there a role for computerized decision support for drug dosing in general practice? A questionnaire survey. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics 2000;25(5):373‐7. - PubMed
Garcia‐Alamino 2010
Garg 2005
-
- Garg AX, Adhikari NK, McDonald H, Rosas‐Arellano M, Devereaux PJ, Beyene J, et al. Effects of computerized clinical decision support systems on practitioner performance and patient outcomes: a systematic review. JAMA 2005;293(10):1223‐38. - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Woodcock J, Brozek J, Helfand M, et al. GRADE guidelines: 7. Rating the quality of evidence ‐ inconsistency. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64:1294‐302. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hozo 2005
Ioannidis 2007
Kawamoto 2005
Kuperman 2003
-
- Kuperman GJ, Gibson RF. Computer physician order entry: benefits, costs, and issues. Annals of Internal Medicine 2003;139(1):31‐9. - PubMed
McDonald 1976a
-
- McDonald CJ. Protocol‐based computer reminders, the quality of care and the non‐perfectability of man. New England Journal of Medicine 1976;295(24):1351‐5. - PubMed
Moher 2009
Mollon 2009
Moore 1984a
-
- Moore RD, Smith CR, Lietman PS. Association of aminoglycoside plasma levels with therapeutic outcome in gram‐negative pneumonia. American Journal of Medicine 1984;77(4):657‐62. [Moore 1984a] - PubMed
Moore 1984b
-
- Moore RD, Smith CR, Lietman PS. The association of aminoglycoside plasma levels with mortality in patients with gram‐negative bacteremia. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1984;149(3):443‐8. [Moore 1984b] - PubMed
Moore 1987
-
- Moore RD, Lietman PS, Smith CR. Clinical response to aminoglycoside therapy: importance of the ratio of peak concentration to minimal inhibitory concentration. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1987;155(1):93‐9. - PubMed
National Asthma 2002
-
- National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Expert Panel Report: guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma update on selected topics ‐ 2002. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2002;110(5 Suppl):S141‐219. - PubMed
Nieuwlaat 2011a
Pearson 2009
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Robertson 2010
-
- Robertson J, Walkom E, Pearson SA, Hains I, Williamsone M, Newby D. The impact of pharmacy computerised clinical decision support on prescribing, clinical and patient outcomes: a systematic review of the literature. International Journal of Pharmacy Practice 2010;2:69‐87. - PubMed
Rolfe 1995
Shojania 2009
Ukoumunne 1999
Yourman 2008
-
- Yourman L, Concato J, Agostini JV. Use of computer decision support interventions to improve medication prescribing in older adults: a systematic review. American Journal of Geriatric Pharmacotherapy 2008;6(2):119‐29. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Durieux 2008
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

