Impact of reconstituted cytosol on protein stability
- PMID: 24218610
- PMCID: PMC3845188
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1312678110
Impact of reconstituted cytosol on protein stability
Abstract
Protein stability is usually studied in simple buffered solutions, but most proteins function inside cells, where the heterogeneous and crowded environment presents a complex, nonideal system. Proteins are expected to behave differently under cellular crowding owing to two types of contacts: hard-core repulsions and weak, chemical interactions. The effect of hard-core repulsions is purely entropic, resulting in volume exclusion owing to the mere presence of the crowders. The weak interactions can be repulsive or attractive, thus enhancing or diminishing the excluded volume, respectively. We used a reductionist approach to assess the effects of intracellular crowding. Escherichia coli cytoplasm was dialyzed, lyophilized, and resuspended at two concentrations. NMR-detected amide proton exchange was then used to quantify the stability of the globular protein chymotrypsin inhibitor 2 (CI2) in these crowded solutions. The cytosol destabilizes CI2, and the destabilization increases with increasing cytosol concentration. This observation shows that the cytoplasm interacts favorably, but nonspecifically, with CI2, and these interactions overcome the stabilizing hard-core repulsions. The effects of the cytosol are even stronger than those of homogeneous protein crowders, reinforcing the biological significance of weak, nonspecific interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


 corresponding to the vertical sides of Fig. 1. Black bars,
corresponding to the vertical sides of Fig. 1. Black bars,  in reconstituted cytosol (100.0 g dry weight/L); red bars,
in reconstituted cytosol (100.0 g dry weight/L); red bars,  values in dilute solution. Data are shown for residues observed in both proteins whose
values in dilute solution. Data are shown for residues observed in both proteins whose  values are statistically different from zero.
values are statistically different from zero.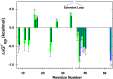
 corresponding to the horizontal sides of Fig. 1. Green bars,
corresponding to the horizontal sides of Fig. 1. Green bars,  for I57A;I37H variant; blue bars,
for I57A;I37H variant; blue bars,  values for I29A;I37H variant. Data are shown for residues observed in both proteins under both conditions whose
values for I29A;I37H variant. Data are shown for residues observed in both proteins under both conditions whose  values are statistically different from zero.
values are statistically different from zero.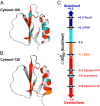
 in 100.0 g dry weight/L (A) and 130.0 g dry weight/L (B) of reconstituted cytosol [blue,
in 100.0 g dry weight/L (A) and 130.0 g dry weight/L (B) of reconstituted cytosol [blue,  (kcal/mol) > 0.3; cyan,
(kcal/mol) > 0.3; cyan,  ; orange,
; orange,  ; red,
; red,  ]. White areas denote prolines and amide protons that either exchanged completely before the second time point or were too broad to observe under one or more conditions. Changes in the average global stability of CI2 under crowded conditions (C). The SDs of the mean of the
]. White areas denote prolines and amide protons that either exchanged completely before the second time point or were too broad to observe under one or more conditions. Changes in the average global stability of CI2 under crowded conditions (C). The SDs of the mean of the  values for protons that exchange upon global unfolding (41) are indicated by the size of the circle. Cytosol-100 and Cytosol-130 indicate 100.0 g dry weight/L and 130.0 g dry weight/L of the reconstituted cytosol, respectively at pH 6.5, 20 °C. Ficoll (100 g/L, pH 5.4, 37 °C) data are from ref. . PVP (100 g/L, pH 5.4, 37 °C) data are from ref. . BSA (100 g/L, pH 6.5, 20 °C) and lysozyme (100 g/L, pH 6.5, 20 °C) data are from ref. . The lysate, BSA, and lysozyme data were acquired at 20 °C. The stabilizing effects Ficoll and PVP are probably slightly exaggerated because these data were acquired at 37 °C, and crowding-induced stability is predicted to increase with increasing temperature (57).
values for protons that exchange upon global unfolding (41) are indicated by the size of the circle. Cytosol-100 and Cytosol-130 indicate 100.0 g dry weight/L and 130.0 g dry weight/L of the reconstituted cytosol, respectively at pH 6.5, 20 °C. Ficoll (100 g/L, pH 5.4, 37 °C) data are from ref. . PVP (100 g/L, pH 5.4, 37 °C) data are from ref. . BSA (100 g/L, pH 6.5, 20 °C) and lysozyme (100 g/L, pH 6.5, 20 °C) data are from ref. . The lysate, BSA, and lysozyme data were acquired at 20 °C. The stabilizing effects Ficoll and PVP are probably slightly exaggerated because these data were acquired at 37 °C, and crowding-induced stability is predicted to increase with increasing temperature (57).Similar articles
-
Protein crowder charge and protein stability.Biochemistry. 2014 Mar 18;53(10):1601-6. doi: 10.1021/bi4016346. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 24552162
-
An osmolyte mitigates the destabilizing effect of protein crowding.Protein Sci. 2014 Sep;23(9):1161-4. doi: 10.1002/pro.2510. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Protein Sci. 2014. PMID: 24963990 Free PMC article.
-
Volume exclusion and soft interaction effects on protein stability under crowded conditions.Biochemistry. 2010 Aug 24;49(33):6984-91. doi: 10.1021/bi100727y. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20672856 Free PMC article.
-
Macromolecular Crowding Is More than Hard-Core Repulsions.Annu Rev Biophys. 2022 May 9;51:267-300. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-091321-071829. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Annu Rev Biophys. 2022. PMID: 35239418 Review.
-
Revisiting a dogma: the effect of volume exclusion in molecular crowding.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2015 Feb;30:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2014.10.005. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2015. PMID: 25464122 Review.
Cited by
-
Calcineurin in a Crowded World.Biochemistry. 2016 Jun 7;55(22):3092-101. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00059. Epub 2016 May 19. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27187005 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen exchange of disordered proteins in Escherichia coli.Protein Sci. 2015 May;24(5):706-13. doi: 10.1002/pro.2643. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Protein Sci. 2015. PMID: 25611326 Free PMC article.
-
Rotational and Translational Diffusion of Proteins as a Function of Concentration.ACS Omega. 2019 Nov 27;4(24):20654-20664. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b02835. eCollection 2019 Dec 10. ACS Omega. 2019. PMID: 31858051 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Crowding Regulates Transcription.Biophys J. 2020 May 5;118(9):2117-2129. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.11.007. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 31818468 Free PMC article.
-
Macromolecular crowding links ribosomal protein gene dosage to growth rate in Vibrio cholerae.BMC Biol. 2020 Apr 29;18(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12915-020-00777-5. BMC Biol. 2020. PMID: 32349767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zimmerman SB, Trach SO. Estimation of macromolecule concentrations and excluded volume effects for the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1991;222(3):599–620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

