In-vivo dark-field and phase-contrast x-ray imaging
- PMID: 24220606
- PMCID: PMC3826096
- DOI: 10.1038/srep03209
In-vivo dark-field and phase-contrast x-ray imaging
Abstract
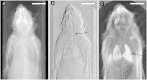
Novel radiography approaches based on the wave nature of x-rays when propagating through matter have a great potential for improved future x-ray diagnostics in the clinics. Here, we present a significant milestone in this imaging method: in-vivo multi-contrast x-ray imaging of a mouse using a compact scanner. Of particular interest is the enhanced contrast in regions related to the respiratory system, indicating a possible application in diagnosis of lung diseases (e.g. emphysema).
Figures
References
-
- Pfeiffer F., Weitkamp T., Bunk O. & David C. Phase retrieval and differential phase-contrast imaging with low-brilliance X-ray sources. Nat. Phys. 2, 258–261 (2006).
-
- Pfeiffer F., Kottler C., Bunk O. & David C. Hard x-ray phase tomography with low-brilliance sources. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 1–4 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Pfeiffer F. et al. Hard-x-ray dark-field imaging using a grating interferometer. Nat. Mater. 7, 134–137 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Bech M. et al. Quantitative X-ray dark-field computed tomography. Phys Med Biol. 55, 5529–5539 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

