Co-regulation of primary mouse hepatocyte viability and function by oxygen and matrix
- PMID: 24222008
- PMCID: PMC4110975
- DOI: 10.1002/bit.25152
Co-regulation of primary mouse hepatocyte viability and function by oxygen and matrix
Abstract
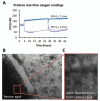
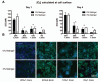
Although oxygen and extracellular matrix cues both influence differentiation state and metabolic function of primary rat and human hepatocytes, relatively little is known about how these factors together regulate behaviors of primary mouse hepatocytes in culture. To determine the effects of pericellular oxygen tension on hepatocellular function, we employed two methods of altering oxygen concentration in the local cellular microenvironment of cells cultured in the presence or absence of an extracellular matrix (Matrigel) supplement. By systematically altering medium depth and gas phase oxygen tension, we created multiple oxygen regimes (hypoxic, normoxic, and hyperoxic) and measured the local oxygen concentrations in the pericellular environment using custom-designed oxygen microprobes. From these measurements of oxygen concentrations, we derived values of oxygen consumption rates under a spectrum of environmental contexts, thus providing the first reported estimates of these values for primary mouse hepatocytes. Oxygen tension and matrix microenvironment were found to synergistically regulate hepatocellular survival and function as assessed using quantitative image analysis for cells stained with vital dyes, and assessment of secretion of albumin. Hepatocellular viability was affected only at strongly hypoxic conditions. Surprisingly, albumin secretion rates were greatest at a moderately supra-physiological oxygen concentration, and this effect was mitigated at still greater supra-physiological concentrations. Matrigel enhanced the effects of oxygen on retention of function. This study underscores the importance of carefully controlling cell density, medium depth, and gas phase oxygen, as the effects of these parameters on local pericellular oxygen tension and subsequent hepatocellular function are profound.
Keywords: albumin secretion; hepatocyte; mouse; oxygen consumption; static culture.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
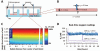

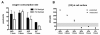
References
-
- Arteel GE, Iimuro Y, Yin M, Raleigh JA, Thurman RG. Chronic enteral ethanol treatment causes hypoxia in rat liver tissue in vivo. Hepatology. 1997;25(4):920–926. - PubMed
-
- Chandra P, Lecluyse E, Brouwer K. Optimization of culture conditions for determining hepatobiliary disposition of taurocholate in sandwich-cultured rat hepatocytes. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal. 2001;37(6):380–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

