Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children with Down syndrome: a retrospective analysis from the Ponte di Legno study group
- PMID: 24222333
- PMCID: PMC3879907
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-06-509463
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children with Down syndrome: a retrospective analysis from the Ponte di Legno study group
Abstract
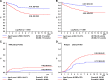
Children with Down syndrome (DS) have an increased risk of B-cell precursor (BCP) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The prognostic factors and outcome of DS-ALL patients treated in contemporary protocols are uncertain. We studied 653 DS-ALL patients enrolled in 16 international trials from 1995 to 2004. Non-DS BCP-ALL patients from the Dutch Child Oncology Group and Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster were reference cohorts. DS-ALL patients had a higher 8-year cumulative incidence of relapse (26% ± 2% vs 15% ± 1%, P < .001) and 2-year treatment-related mortality (TRM) (7% ± 1% vs 2.0% ± <1%, P < .0001) than non-DS patients, resulting in lower 8-year event-free survival (EFS) (64% ± 2% vs 81% ± 2%, P < .0001) and overall survival (74% ± 2% vs 89% ± 1%, P < .0001). Independent favorable prognostic factors include age <6 years (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.58, P = .002), white blood cell (WBC) count <10 × 10(9)/L (HR = 0.60, P = .005), and ETV6-RUNX1 (HR = 0.14, P = .006) for EFS and age (HR = 0.48, P < .001), ETV6-RUNX1 (HR = 0.1, P = .016) and high hyperdiploidy (HeH) (HR = 0.29, P = .04) for relapse-free survival. TRM was the major cause of death in ETV6-RUNX1 and HeH DS-ALLs. Thus, while relapse is the main contributor to poorer survival in DS-ALL, infection-associated TRM was increased in all protocol elements, unrelated to treatment phase or regimen. Future strategies to improve outcome in DS-ALL should include improved supportive care throughout therapy and reduction of therapy in newly identified good-prognosis subgroups.
Figures

References
-
- Hasle H, Clemmensen IH, Mikkelsen M. Risks of leukaemia and solid tumours in individuals with Down’s syndrome. Lancet. 2000;355(9199):165–169. - PubMed
-
- Forestier E, Izraeli S, Beverloo B, et al. Cytogenetic features of acute lymphoblastic and myeloid leukemias in pediatric patients with Down syndrome: an iBFM-SG study. Blood. 2008;111(3):1575–1583. - PubMed
-
- Hertzberg L, Vendramini E, Ganmore I, et al. Down syndrome acute lymphoblastic leukemia, a highly heterogeneous disease in which aberrant expression of CRLF2 is associated with mutated JAK2: a report from the International BFM Study Group. Blood. 2010;115(5):1006–1017. - PubMed
-
- Dördelmann M, Schrappe M, Reiter A, et al. Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster Group. Down’s syndrome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: clinical characteristics and treatment outcome in four consecutive BFM trials. Leukemia. 1998;12(5):645–651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

