Development and validation of an ELISA at acidic pH for the quantitative determination of IL-13 in human plasma and serum
- PMID: 24222716
- PMCID: PMC3810116
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/290670
Development and validation of an ELISA at acidic pH for the quantitative determination of IL-13 in human plasma and serum
Abstract
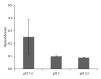
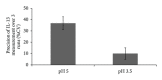
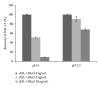
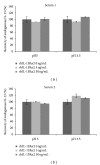
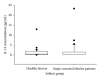
A novel sandwich ELISA for the quantitative and sensitive determination of IL-13 in human serum and plasma was established. The assay employs an incubation step at acidic pH, which was shown to decrease nonspecific binding and interference from IL-13 binding proteins. The assay was validated and was shown to be accurate and precise over the entire quantification range (0.59 to 68.4 pg/mL in human EDTA plasma). The validated assay was successfully applied to samples from healthy volunteers and patients with atopic seasonal rhinitis. The assay is suitable for use in clinical trials to monitor efficacy or pharmacodynamic effects of drug candidates.
Figures

References
-
- Mitchell J, Dimov V, Townley RG. IL-13 and the IL-13 receptor as therapeutic targets for asthma and allergic disease. Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs. 2010;11(5):527–534. - PubMed
-
- Wills-Karp M. Interleukin-13 in asthma pathogenesis. Immunological Reviews. 2004;202:175–190. - PubMed
-
- Becker AB. Challenges to treatment goals and outcomes in pediatric asthma. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2002;109(6):S533–S538. - PubMed
-
- Noah TL, Tudor GE, Ivins SS, Murphy PC, Peden DB, Henderson FW. Repeated measurement of nasal lavage fluid chemokines in school-age children with asthma. Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. 2006;96(2):304–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

