Cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism and risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 24222746
- PMCID: PMC3814096
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/689048
Cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism and risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a meta-analysis
Abstract
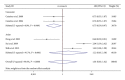
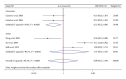
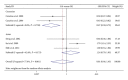
Recently, there have been a number of studies on the association between cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism and nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk. However, the results of previous reports remain controversial and ambiguous. Thus, we performed a meta-analysis to explore more precisely the association between cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism and the risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. No significant association was found between cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism and nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk in total population analysis. In the subgroup meta-analysis by ethnicity, a negative association was shown in Caucasian subgroup, and no significant association in any genetic models among Asians was observed. In summary, positive results have been shown on the search for polymorphic variants influencing the risk of NPC. This meta-analysis provides evidence of the association between CCND1 G870A polymorphism and NPC risk, supporting the hypothesis that CCND1 870A allele probably acts as an important NPC protective factor in Caucasians but not in Asians. Since the results of our meta-analysis are preliminary and may be biased by the relatively small number of subjects, they still need to be validated by well-designed studies using larger samples in the future.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism and risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a case-control study and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 19;9(11):e113299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113299. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25409185 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin D1 (CCND1) G870A gene polymorphism is an ethnicity-dependent risk factor for digestive tract cancers: a meta-analysis comprising 20,271 subjects.Cancer Epidemiol. 2012 Apr;36(2):106-15. doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2011.04.007. Epub 2011 May 24. Cancer Epidemiol. 2012. PMID: 21606015
-
Cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism is a risk factor for esophageal cancer among Asians.Cancer Invest. 2012 Nov;30(9):630-6. doi: 10.3109/07357907.2012.726385. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Cancer Invest. 2012. PMID: 23020291
-
The association between CCND1 G870A polymorphism and colorectal cancer risk: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Oct;96(42):e8269. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008269. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29049220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AA genotype of cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism increases breast cancer risk: Findings of a case-control study and meta-analysis.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Oct;120(10):16452-16466. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28800. Epub 2019 Jun 26. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31243808
Cited by
-
Radiotherapy induces cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the ATM and Smad pathways.Cancer Biol Ther. 2017 Sep 2;18(9):681-693. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2017.1360442. Cancer Biol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28799829 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin D1 (CCND1) G870A polymorphisms and cervical cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis based on ten case-control studies.Tumour Biol. 2014 Jul;35(7):6913-8. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-1929-6. Epub 2014 Apr 16. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24737585
-
Cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism and risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a case-control study and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 19;9(11):e113299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113299. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25409185 Free PMC article.
-
Limb-bud and Heart (LBH) functions as a tumor suppressor of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by inducing G1/S cell cycle arrest.Sci Rep. 2015 Jan 5;5:7626. doi: 10.1038/srep07626. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25557837 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between the hOGG1 rs1052133 Polymorphism and the Occurrence of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241246457. doi: 10.1177/15330338241246457. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38836311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang ET, Adami H. The enigmatic epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention. 2006;15(10):1765–1777. - PubMed
-
- Hwang CF, Cho CL, Huang CC, et al. Loss of cyclin D1 and p16 expression correlates with local recurrence in nasopharyngeal carcinoma following radiotherapy. Annals of Oncology. 2002;13(8):1246–1251. - PubMed
-
- Hui AB, Or YY, Takano H, et al. Array-based comparative genomic hybridization analysis identified cyclin D1 as a target oncogene at 11q13.3 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Research. 2005;65(18):8125–8133. - PubMed
-
- Knudsen KE, Diehl JA, Haiman CA, Knudsen ES. Cyclin D1: polymorphism, aberrant splicing and cancer risk. Oncogene. 2006;25(11):1620–1628. - PubMed
-
- Pabalan N, Bapat B, Sung L, Jarjanazi H, Francisco-Pabalan O, Ozcelik H. Cyclin D1 Pro241Pro (CCND1-G870A) polymorphism is associated with increased cancer risk in human populations: a meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention. 2008;17(10):2773–2781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

