Influence of root exudates on the bacterial degradation of chlorobenzoic acids
- PMID: 24222753
- PMCID: PMC3809935
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/872026
Influence of root exudates on the bacterial degradation of chlorobenzoic acids
Abstract
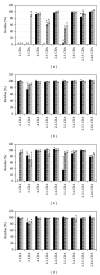
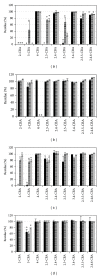
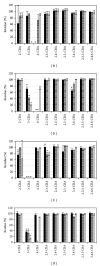
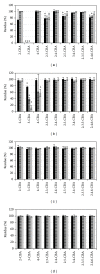
Degradation of chlorobenzoic acids (e.g., products of microbial degradation of PCB) by strains of microorganisms isolated from PCB contaminated soils was assessed. From seven bulk-soil isolates two strains unique in ability to degrade a wider range of chlorobenzoic acids than others were selected, individually and even in a complex mixture of 11 different chlorobenzoic acids. Such a feature is lacking in most tested degraders. To investigate the influence of vegetation on chlorobenzoic acids degraders, root exudates of two plant species known for supporting PCB degradation in soil were tested. While with individual chlorobenzoic acids the presence of plant exudates leads to a decrease of degradation yield, in case of a mixture of chlorobenzoic acids either a change in bacterial degradation specificity, associated with 3- and 4-chlorobenzoic acid, or an extension of the spectrum of degraded chlorobenzoic acids was observed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Degradation of 2-chlorobenzoic and 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acids in soil columns by Pseudomonas stutzeri.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 1993;38(5):376-8. doi: 10.1007/BF02898759. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 1993. PMID: 8262447
-
Genetic control of degradation of chlorinated benzoic acids in Arthrobacter globiformis, Corynebacterium sepedonicum and Pseudomonas cepacia strains.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jun 15;65(2):171-6. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90299-p. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991. PMID: 1884993
-
Isolation and preliminary characterization of a 2-chlorobenzoate degrading Pseudomonas.Can J Microbiol. 1989 Apr;35(4):439-43. doi: 10.1139/m89-067. Can J Microbiol. 1989. PMID: 2743216
-
Degradation of 2-chlorobenzoic and 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acids in pure culture by Pseudomonas stutzeri.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 1993;38(5):371-5. doi: 10.1007/BF02898758. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 1993. PMID: 8262446
-
Biodegradation of 4-chlorobenzoic acid by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01 NC.Biodegradation. 2011 Jun;22(3):509-16. doi: 10.1007/s10532-010-9423-3. Epub 2010 Oct 6. Biodegradation. 2011. PMID: 20924649
Cited by
-
Changes in fatty acid composition of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia KB2 during co-metabolic degradation of monochlorophenols.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Dec;32(12):198. doi: 10.1007/s11274-016-2160-y. Epub 2016 Oct 18. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27757793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matějů V. Kompendium Sanačních Technologií. Chrudim, Czech Republic: Vodní zdroje Ekomonitor spol s. r. o.; 2006.
-
- Adebusoye SA, Picardal FW, Ilori MO, Amund OO. Influence of chlorobenzoic acids on the growth and degradation potentials of PCB-degrading microorganisms. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2008;24(7):1203–1208.
-
- Scholten JD, Chang K-H, Babbitt PC, Charest H, Sylvestre M, Dunaway-Mariano D. Novel enzymic hydrolytic dehalogenation of a chlorinated aromatic. Science. 1991;253(5016):182–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

