Masquerading Mycobacterium: Plastic surgeon to the rescue
- PMID: 24223001
- PMCID: PMC3822478
- DOI: 10.1177/229255030501300110
Masquerading Mycobacterium: Plastic surgeon to the rescue
Abstract
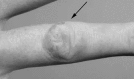
A patient with a Mycobacterium marinum infection of the hand is described. The present case illustrates that M marinum infection may mimic common skin conditions such as eczema, and fungal and parasitic infestations. Key elements in the diagnosis and management of this infection are a high index of suspicion, a detailed history of recreational or occupational exposure to exotic fish, tissue biopsy, wound culture and prompt empirical antibiotic therapy. Once in vitro organism sensitivities are obtained, antibiotic treatment may last for up to 24 months. Surgical drainage and debridement are an important supplement to antimicrobial therapy when subcutaneous structures are involved, as in the present report. Invasive digital and hand infections can rapidly result in permanent residual stiffness, deformity and loss of function; therefore, it is important to raise awareness of the condition among those considered to be at risk.
On décrit ici le cas d’un patient atteint d’une infection à Mycobacterium marinum au niveau de la main. Ce cas illustre que l’infection à M. marinum peut prendre l’apparence de maladies dermatologiques, comme l’eczéma, ou d’infestations fongiques et parasitaires. Les éléments clés du diagnostic et du traitement de cette infection sont tout d’abord un fort indice de soupçon, une anamnèse détaillée des activités récréatives et professionnelles ayant pu mener à l’exposition à des poissons exotiques, la biopsie tissulaire, la culture de plaie et l’instauration rapide d’une antibiothérapie empirique. Une fois les résultats des cultures obtenus, l’antibiothérapie peut durer jusqu’à 24 mois. Le drainage et le débridement chirurgicaux sont d’importants compléments à l’antibiothérapie lorsque les structures sous-cutanées sont touchées, comme dans le cas présent. L’infection invasive des doigts et de la main peut rapidement entraîner une raideur, une déformation et une perte de fonction résiduelles permanentes. Par conséquent, il est important de sensibiliser la communauté médicale à cette maladie chez les sujets à risque.
Keywords: Fish tank granuloma; Immunosuppresion; Mycobacterium.
Figures
References
-
- Bhatty MA, Turner DP, Chamberlain ST. Mycobacterium marinum hand infection: Case reports and review of literature. Br J Plast Surg. 2000;53:161–5. - PubMed
-
- Raphael JK. Mycobacterium marinum. http://www.emedicine.com/med/topic1538.htm. (Version current at December 2, 2004)
-
- Kullavanijaya P, Sirimachan S, Bhuddhavudhikrai P. Mycobacterium marinum cutaneous infection acquired from occupations and hobbies. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:504–7. - PubMed
-
- Hurst LC, Amadio PC, Badalamente MA, Ellstein JL, Dattwyler RJ. Mycobacterium marinum infections of the hand. J Hand Surg [Am] 1987;12:428–35. - PubMed
-
- Feddersen A, Kunkel J, Jonas D, Engel V, Bhakdi S, Husmann M. Infection of the upper extremity by Mycobacterium marinum in a 3-year-old boy – diagnosis by 16S-rDNA analysis. Infection. 1996;24:47–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources