Solo hand surgery
- PMID: 24223015
- PMCID: PMC3822453
- DOI: 10.1177/229255030501300306
Solo hand surgery
Abstract
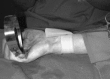
Unassisted hand surgery is being undertaken by necessity for both elective and emergency cases, due to hospital resource restrictions. The authors outline the principles of local anesthesia, surgeon-controlled tourniquet techniques, and a number of new instruments which allow a surgeon to work in comfort and safety, unassisted. The traditional surgical instruments designed for the days when trained surgical assistants were available to hold them are no longer suitable. We are entering a new era of surgical design with safer instruments that can complement our skills rather than challenge them. There are significant cost savings and efficiency when hand procedures are undertaken in the emergency and outpatient clinic settings.
Une opération non assistée de la main est entreprise par nécessité tant dans des cas non urgents qu’urgents, en raison des compressions aux ressources hospitalières. Les auteurs exposent les principes de l’anesthésie locale, les techniques de garrot contrôlées par le chirurgien et un certain nombre de nouveaux instruments qui permettent au chirurgien de travailler à l’aise et en sécurité, sans aide. Les instruments chirurgicaux classiques conçus pour l’époque où des assistants chirurgicaux étaient disponibles pour les tenir ne conviennent plus. S’ouvre une époque de conception chirurgicale où des instruments plus sécuritaires peuvent compléter nos aptitudes plutôt que les compliquer. D’importantes économies et une plus grande efficacité sont constatées lorsque des opérations de la main sont entreprises en urgence et en consultations externes.
Keywords: Anesthesia in hand surgery; CHESS system in hand surgery; Hemostasis in hand surgery; Magnetic hand retraction; Unassisted surgery.
Figures



References
-
- Mahoney JL, Lofahy NM, Chow ITS, Hudson A. Carpal tunnel syndrome: A quality assurance evaluation of surgical treatment. Ann R Coll Physicians Surg Can. 1993;25:20–3.
-
- Guirgus EM, Bell MSG. The wrist tourniquet: An alternative technique in hand surgery. J Hand Surg. 1990;15A:516–9. - PubMed
-
- Livingston JD. Driving Force: The Natural Magic of Magnets. Cambridge: Harvard University Press; 1996. pp. 87–113.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
