Activation of IFN-γ/STAT/IRF-1 in hepatic responses to Klebsiella pneumoniae infection
- PMID: 24223208
- PMCID: PMC3819302
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079961
Activation of IFN-γ/STAT/IRF-1 in hepatic responses to Klebsiella pneumoniae infection
Abstract
Background: Klebsiella pneumoniae-caused liver abscess (KLA) has become a health problem in Taiwan and is continually reported in other countries. Diabetes mellitus, the most common metabolic disorder, underlies half of the KLA patients in Taiwan. The clinical impact of KLA has been well-documented. Nevertheless, the molecular basis regarding how K. pneumoniae causes liver infection, particularly in diabetic individuals, remains unclear.
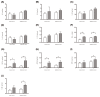
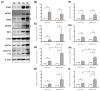
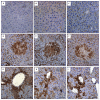
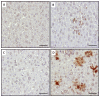
Methodology/principle findings: Auto-bioluminescence-expressing K. pneumoniae was inoculated into diabetic mice and age-match naïve control. With the use of in vivo imaging system, translocation of the bioluminescence-expressing K. pneumoniae from intestine to extraintestinal organs, mainly the liver, was noted in 80% of the diabetic mice, whereas the same bacteria causes extraintestinal infections in only 31% of naïve mice. Besides increased morbidity, the severity of hepatic tissue injury was also enhanced in the K. pneumoniae-infected diabetic mice. Upon K. pneumoniae infection, IFN-γ production was significantly evoked in the liver. To mediate IFN-γ signal, STAT (signal transducers and activators of transcription) 1 and 3 were activated in hepatocytes, and so was the expression of IRF (interferon regulatory factor)-1. Moreover, accumulation of neutrophils which was triggered by prolonged production of IL-1β and MIP-2, and significant increases in the level of active caspase 3 and phospho-eIF2α, were exclusively revealed in the K. pneumoniae-infected diabetic mice.
Conclusion: The activation of IFN-γ/STAT/IRF-1 signaling demonstrated by this work emphasizes the role of IFN-γ for mediating the hepatic response to K. pneumoniae infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

