Mycoplasma pneumoniae associated stroke in a 3-year-old girl
- PMID: 24223604
- PMCID: PMC3819683
- DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2013.56.9.411
Mycoplasma pneumoniae associated stroke in a 3-year-old girl
Abstract
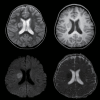
Infectious diseases precede a significant proportion of acute ischemic strokes in children. Here, we report a case of acute ischemic stroke in a 3-year-old girl with a Mycoplasma pneumonia-associated respiratory tract infection. She developed an acquired prothrombotic state of protein S deficiency and had increased fibrinogen and fibrinogen degradation product levels and increased titer of antinuclear antibodies. However, these conditions were completely alleviated at the 1-month follow-up examination. Infection with M. pneumoniae may cause a transient prothrombotic state that can potentially cause a thrombus.
Keywords: Child; Mycoplasma pneumoniae; Stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Mackay MT, Wiznitzer M, Benedict SL, Lee KJ, Deveber GA, Ganesan V, et al. Arterial ischemic stroke risk factors: the International Pediatric Stroke Study. Ann Neurol. 2011;69:130–140. - PubMed
-
- Ovetchkine P, Brugieres P, Seradj A, Reinert P, Cohen R. An 8-y-old boy with acute stroke and radiological signs of cerebral vasculitis after recent Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Scand J Infect Dis. 2002;34:307–309. - PubMed
-
- Ryu JS, Kim HJ, Sung IY, Ko TS. Posterior cerebral artery occlusion after Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection associated with genetic defect of MTHFR C677T. J Child Neurol. 2009;24:891–894. - PubMed
-
- Nakahata C, Kittka E, Fujii H, Sakano T, Usui T. A case of cerebral infarction associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Hiroshima J Med Sci. 1983;32:277–279. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

