Association of serum retinol binding protein 4 with atherogenic dyslipidemia in morbid obese patients
- PMID: 24223837
- PMCID: PMC3817034
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078670
Association of serum retinol binding protein 4 with atherogenic dyslipidemia in morbid obese patients
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2013;8(12). doi:10.1371/annotation/4ee4f5f7-519f-402c-8ed2-dff0cc6c5e48
Abstract
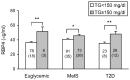
Retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4) is an adipokine that may contribute to the development of insulin resistance. However, how this adipokine is affected and its possible involvement in lipid metabolism in obese patients with varying degrees of insulin resistance is yet to be determined. A total of 299 middle-aged morbid obese patients (BMI>40 kg/m(2)) were divided in euglycemic, metabolic syndrome or type 2 diabetic. Anthropometric measurements, biochemical variables and systemic RBP4 levels were determined. RBP4 levels were significantly higher in patients with metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes than in euglycemic subjects (42.9±14.6; 42.3±17.0 and 37.4±11.7 µg/ml, respectively) and correlated with triglycerides but not with those of HOMA-IR in the whole population. The multivariate regression model revealed that triglycerides were the strongest predictor of systemic RBP4 levels. Analysis of lipoprotein subfractions in a subpopulation of 80 subjects showed an altered profile of insulin resistant states characterized by higher VLDL, sdLDL and small HDL percentages and lower large HDL percentage. Although RBP4 levels correlated significantly with LDL particle size and small HDL percentage, the latter parameter was independently associated only with RBP4. Our study reveals that systemic RBP4 levels could play an important role in lipid metabolism in morbid obesity, increasing triglyceride levels and contributing to the formation of small HDL.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Correlation of retinol binding protein 4 with metabolic indexes of glucose and lipid, bile cholesterol saturation index].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015 Jun;40(6):657-65. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2015.06.014. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015. PMID: 26164516 Chinese.
-
Association among retinol-binding protein 4, small dense LDL cholesterol and oxidized LDL levels in dyslipidemia subjects.Clin Biochem. 2012 Jun;45(9):619-22. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.02.022. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Clin Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22426023
-
Beyond low-density lipoprotein: addressing the atherogenic lipid triad in type 2 diabetes mellitus and the metabolic syndrome.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2005;5(6):379-87. doi: 10.2165/00129784-200505060-00005. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2005. PMID: 16259526 Review.
-
Circulating retinol-binding protein 4 and metabolic syndrome in the elderly.Wien Med Wochenschr. 2011 Nov;161(21-22):505-10. doi: 10.1007/s10354-011-0885-7. Epub 2011 Apr 4. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2011. PMID: 21442217
-
Pathophysiology of Diabetic Dyslipidemia.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2018 Sep 1;25(9):771-782. doi: 10.5551/jat.RV17023. Epub 2018 Jul 12. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2018. PMID: 29998913 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cushing's syndrome is associated with altered adipokine profile.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 6;13:1032329. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1032329. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36561568 Free PMC article.
-
Reproducibility of Retinol Binding Protein 4 and Omentin-1 Measurements over a Four Months Period: A Reliability Study in a Cohort of 207 Apparently Healthy Participants.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 24;10(9):e0138480. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138480. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26402656 Free PMC article.
-
Altering retinol binding protein 4 levels in hepatitis C: Inflammation and steatosis matter.Virulence. 2020 Dec;11(1):1501-1511. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1838742. Virulence. 2020. PMID: 33135589 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Dimorphism in the Association of Serum Retinol-Binding Protein-4 With Long-Term Dynamic Metabolic Profiles in Non-Diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 May 11;13:880467. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.880467. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35634496 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasensitive nano-aptasensor for monitoring retinol binding protein 4 as a biomarker for diabetes prognosis at early stages.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 17;10(1):594. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-57396-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31953481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, et al. (2010) Heart disease and stroke statistics (a report from the American Heart Association). Circulation 121: 46–215. - PubMed
-
- Glass CK, Witztum JL (2001) Atherosclerosis:The road ahead. Cell 104: 503–516. - PubMed
-
- Kontush A, Chapman MJ (2006) Antiatherogenic small, dense HDL -guardian angel of the arterial wall? Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 3: 144–153. - PubMed
-
- Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F, Peroni OD, et al. (2005) Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature 436: 356–362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

