Functional role of Mst1/Mst2 in embryonic stem cell differentiation
- PMID: 24224013
- PMCID: PMC3818222
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079867
Functional role of Mst1/Mst2 in embryonic stem cell differentiation
Abstract
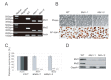
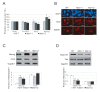
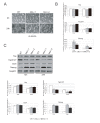
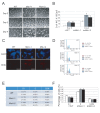
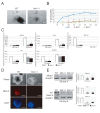
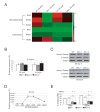
The Hippo pathway is an evolutionary conserved pathway that involves cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and organ size regulation. Mst1 and Mst2 are central components of this pathway that are essential for embryonic development, though their role in controlling embryonic stem cells (ES cells) has yet to be exploited. To further understand the Mst1/Mst2 function in ES cell pluripotency and differentiation, we derived Mst1/Mst2 double knockout (Mst-/-) ES cells to completely perturb Hippo signaling. We found that Mst-/- ES cells express higher level of Nanog than wild type ES cells and show differentiation resistance after LIF withdrawal. They also proliferate faster than wild type ES cells. Although Mst-/- ES cells can form embryoid bodies (EBs), their differentiation into tissues of three germ layers is distorted. Intriguingly, Mst-/- ES cells are unable to form teratoma. Mst-/- ES cells can differentiate into mesoderm lineage, but further differentiation to cardiac lineage cells is significantly affected. Microarray analysis revealed that ligands of non-canonical Wnt signaling, which is critical for cardiac progenitor specification, are significantly repressed in Mst-/- EBs. Taken together our results showed that Mst1/Mst2 are required for proper cardiac lineage cell development and teratoma formation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mammalian Mst1 and Mst2 kinases play essential roles in organ size control and tumor suppression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jan 26;107(4):1431-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911409107. Epub 2010 Jan 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20080598 Free PMC article.
-
Hippo signaling is a potent in vivo growth and tumor suppressor pathway in the mammalian liver.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jan 26;107(4):1437-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911427107. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20080689 Free PMC article.
-
Hippo/Yap signaling controls epithelial progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation in the embryonic and adult lung.J Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Feb;7(1):35-47. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mju046. Epub 2014 Dec 5. J Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25480985 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Hippo signaling pathway and mechanotransduction in tuning embryoid body formation and differentiation.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Jun;235(6):5072-5083. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29455. Epub 2020 Jan 17. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31951024 Review.
-
The DeMSTification of mammalian Ste20 kinases.Curr Biol. 2009 May 26;19(10):R421-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.04.022. Curr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19467213 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential localization of A-Raf regulates MST2-mediated apoptosis during epithelial differentiation.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Aug;23(8):1283-95. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.2. Epub 2016 Feb 19. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 26891695 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Signatures and Networks of Cardiomyocyte Differentiation in Humans and Mice.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Sep 4;21:696-711. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.07.011. Epub 2020 Jul 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 32769060 Free PMC article.
-
Hippo-YAP/TAZ signalling in organ regeneration and regenerative medicine.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Apr;20(4):211-226. doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0086-y. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30546055 Review.
-
Hippo-YAP signaling controls lineage differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells through modulating the formation of super-enhancers.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jul 27;48(13):7182-7196. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa482. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32510157 Free PMC article.
-
NF2 is Essential for Human Endoderm Development.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 May;12(17):e2410909. doi: 10.1002/advs.202410909. Epub 2025 Feb 8. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39921490 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

