Low-intensity therapy in adults with Burkitt's lymphoma
- PMID: 24224624
- PMCID: PMC3901044
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1308392
Low-intensity therapy in adults with Burkitt's lymphoma
Abstract
Background: Burkitt's lymphoma is an aggressive B-cell lymphoma that occurs in children and adults and is largely curable with the use of intensive and toxic chemotherapy. Current treatments are less effective and have more severe side effects in adults and patients with immunodeficiency than in children.
Methods: We studied low-intensity treatment consisting of infused etoposide, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide with vincristine, prednisone, and rituximab (EPOCH-R) in patients with untreated Burkitt's lymphoma. Two EPOCH-R regimens were tested: a standard dose-adjusted combination in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-negative patients (DA-EPOCH-R group) and a lower-dose short-course combination with a double dose of rituximab in HIV-positive patients (SC-EPOCH-RR group).
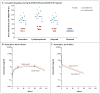
Results: A total of 30 consecutive patients were treated; 19 patients were in the DA-EPOCH-R group, and 11 in the SC-EPOCH-RR group. The overall median age of the patients was 33 years, and 40% were 40 years of age or older; 73% of the patients had intermediate-risk disease, and 10% had high-risk disease. The principal toxic events, fever and neutropenia, were observed during 22% of the DA-EPOCH-R treatment cycles and 10% of the SC-EPOCH-RR treatment cycles. The tumor lysis syndrome developed in 1 patient; no treatment-related deaths occurred. The median cumulative doses of doxorubicin-etoposide and cyclophosphamide administered in the SC-EPOCH-RR group were 47% and 57% lower, respectively, than those administered in the DA-EPOCH-R group. With median follow-up times of 86 months in the DA-EPOCH-R group and 73 months in the SC-EPOCH-RR group, the rates of freedom from progression of disease and overall survival were, respectively, 95% and 100% with DA-EPOCH-R and 100% and 90% with SC-EPOCH-RR. None of the patients died from Burkitt's lymphoma.
Conclusions: In this uncontrolled prospective study, low-intensity EPOCH-R-based treatment was highly effective in adults with sporadic or immunodeficiency-associated Burkitt's lymphoma. (Funded by the National Cancer Institute; ClinicalTrials.gov numbers, NCT00001337 and NCT00006436.).
Figures

Comment in
-
Prolonged low intensity EPOCH-rituximab has improved toxicity in Burkitt lymphoma compared with standard short, high intensity therapy.Cancer Biol Ther. 2014 Sep;15(9):1117-9. doi: 10.4161/cbt.29504. Epub 2014 Jun 11. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24919059 Free PMC article.
-
[Low-dose chemotherapy is highly effective in adults with sporadic or HIV-associated Burkitt's lymphoma].Strahlenther Onkol. 2014 Jun;190(6):600-1. doi: 10.1007/s00066-014-0666-5. Strahlenther Onkol. 2014. PMID: 24967468 German. No abstract available.
References
-
- Burkitt D. A sarcoma involving the jaws in African children. Br J Surg. 1958;46:218–23. - PubMed
-
- Wang ES, Straus DJ, Teruya-Feldstein J, et al. Intensive chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, high-dose methotrexate/ifosfamide, etoposide, and high-dose cytarabine (CODOX-M/IVAC) for human immunodeficiency virus-associated Burkitt lymphoma. Cancer. 2003;98:1196–205. - PubMed
-
- Mead GM, Sydes MR, Walewski J, et al. An international evaluation of CODOX-M and CODOX-M alternating with IVAC in adult Burkitt’s lymphoma: results of United Kingdom Lymphoma Group LY06 study. Ann Oncol. 2002;13:1264–74. - PubMed
-
- Patte C, Auperin A, Michon J, et al. The Société Française d’Oncologie Pédiatrique LMB89 protocol: highly effective multiagent chemotherapy tailored to the tumor burden and initial response in 561 unselected children with B-cell lymphomas and L3 leukemia. Blood. 2001;97:3370–9. - PubMed
-
- Reiter A, Schrappe M, Tiemann M, et al. Improved treatment results in childhood B-cell neoplasms with tailored intensification of therapy: a report of the Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster Group Trial NHL-BFM 90. Blood. 1999;94:3294–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
