The genome portal of the Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute: 2014 updates
- PMID: 24225321
- PMCID: PMC3965075
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt1069
The genome portal of the Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute: 2014 updates
Abstract
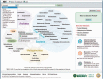
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Joint Genome Institute (JGI), a national user facility, serves the diverse scientific community by providing integrated high-throughput sequencing and computational analysis to enable system-based scientific approaches in support of DOE missions related to clean energy generation and environmental characterization. The JGI Genome Portal (http://genome.jgi.doe.gov) provides unified access to all JGI genomic databases and analytical tools. The JGI maintains extensive data management systems and specialized analytical capabilities to manage and interpret complex genomic data. A user can search, download and explore multiple data sets available for all DOE JGI sequencing projects including their status, assemblies and annotations of sequenced genomes. Here we describe major updates of the Genome Portal in the past 2 years with a specific emphasis on efficient handling of the rapidly growing amount of diverse genomic data accumulated in JGI.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

