Encephalopathy in children with Dravet syndrome is not a pure consequence of epilepsy
- PMID: 24225340
- PMCID: PMC4225757
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1172-8-176
Encephalopathy in children with Dravet syndrome is not a pure consequence of epilepsy
Abstract
Background: Dravet syndrome (DS) is currently considered as an epileptic encephalopathy, a condition in which epilepsy causes deterioration or developmental delay but preliminary data suggested that cognitive course may worsen independently from epilepsy. Our objective was to prospectively analyze the neuropsychological features in a large cohort of DS patients and its relationships with epilepsy and SCN1A mutation.
Methods: 81 examinations were performed in 67 patients with typical DS (9m-24y, 15 longitudinally studied) using Brunet-Lezine (developmental/intelligence quotient [DQ/IQ] and DQ sub-scores), Achenbach, Conners, and a semi-quantitative psychomotor score (SQPS). We studied the correlation between DQ/IQ/SQPS and age, epilepsy characteristics, and whether patients presented SCN1A mutation.
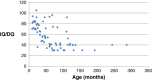
Results: DQ/IQ significantly decreased with age (r = -.53, p < .001), from normal before 2y (mean 80, range 64-105) to low after 3y (mean 48, range 30-69), with hyperactivity and attention disorders hampering learning abilities especially up to 6y. However, raw (not age-adjusted) DQ sub-scores increased with age during the first decade, showing that there is no regression. We did not find any significant correlation between DQ/IQ at last evaluation and epilepsy data, i.e. first seizure (age, type, duration, fever), seizures during the course (type, fever sensitivity), status epilepticus (age of onset, number, fever), photosensitivity, and treatment, except for myoclonus and focal seizures which were associated with a lower QD/IQ after 3y. SCN1A mutated patients (n = 58) seemed to exhibit worse psychomotor course than non-mutated ones (n = 9) (severe SQPS in 26% vs 0%), although their epilepsy tended to be less severe (tonic seizures in 12% vs 44% [p = 0.04], first status epilepticus before 6 m in 26% vs 67% [p = .02], mean number of SE 2.5 vs 4.5 [p = .09]). DQ sub-scores were dissociated throughout the whole course: from onset hand-eye coordination was significantly lower than language, posture and sociability (p < .01). Dissociation seemed to be more frequent in mutated than in non-mutated patients (motor SQPS was normal for in 77% vs 44% [p = 0.017] whereas language SQPS was normal for 47% vs 100%).
Conclusions: Although psychomotor/cognitive delay declines with age, there is no regression. In addition, encephalopathy is not a pure consequence of epilepsy but SCN1A mutation seems to play an additional, direct role.
Figures
References
-
- Dravet C, Bureau M, Oguni H. In: Epileptic Syndromes in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence. Roger J, Bureau M, Dravet C, Genton P, Tassinari CA, Wolff P, editor. London: John Libbey; 2002. Severe Myoclonic Epilepsy in Infancy (Dravet Syndrome) pp. 75–88.
-
- Dravet C, Bureau M, Oguni H, Fukuyama Y, Cokar O. Severe myoclonic epilepsy in infancy: Dravet syndrome. Adv Neurol. 2005;95:71–102. - PubMed
-
- Depienne C, Bouteiller D, Keren B, Cheuret E, Poirier K, Trouillard O, Benyahia B, Quelin C, Carpentier W, Julia S, Afenjar A, Gautier A, Rivier F, Meyer S, Berquin P, Helias M, Py I, Rivera S, Bahi-Buisson N, Gourfinkel-An I, Cazeneuve C, Ruberg M, Brice A, Nabbout R, Leguern E. Sporadic infantile epileptic encephalopathy caused by mutations in PCDH19 resembles Dravet syndrome but mainly affects females. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000381. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000381. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical