High expression of biglycan is associated with poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 24228112
- PMCID: PMC3816819
High expression of biglycan is associated with poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
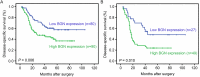
Biglycan (BGN), an extracellular matrix component, has been reported to play a crucial role in the tumor progression of various cancers. However, the relation between the expression of BGN and clinical prognosis has not been studied yet. We therefore carry out the present study to elucidate the role of BGN in predicting outcomes of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). In this study, the expression of BGN in 170 cases of ESCC tissues and matched 46 adjacent non-tumorous tissues was measured by quantitative real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry. Upregulation of BGN occurred in approximately 60% of primary ESCCs compared with their non-tumor counterparts. In addition, high expression of BGN was significantly associated with clinical stage (P = 0.009), tumor invasion (P = 0.006) and lymph node metastasis (P = 0.046). The 5-year disease-specific survival (DSS) in high expression of BGN group is poorer than that in low level expression group (36.8% VS 57.4%, P = 0.006). Stratified analysis according to the pathological stage revealed its discernibility on DSS was only pronounced in patients with advanced clinical stage (P = 0.010). Cox multivariate analysis revealed that pathologic N category (P < 0.001; hazard ratio, 2.482, 95% CI, 1.576-3.909) and BGN expression (P = 0.019; hazard ratio, 1.713, 95% CI, 1.092-2.688) were two independent prognostic factors. The findings of the present study provide evidence that BGN represents a potential novel prognostic biomarker for resected ESCC patients in advanced clinical stage.
Keywords: BGN; ESCC; prognosis.
Figures


References
-
- Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006;24:2137–2150. - PubMed
-
- Wheeler JB, Reed CE. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer. Surg Clin North Am. 2012;92:1077–1087. - PubMed
-
- Hongo M, Nagasaki Y, Shoji T. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer: Orient to Occident. Effects of chronology, geography and ethnicity. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:729–735. - PubMed
-
- Stoner GD, Gupta A. Etiology and chemoprevention of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2001;22:1737–1746. - PubMed
-
- Xiao ZF, Yang ZY, Liang J, Miao YJ, Wang M, Yin WB, Gu XZ, Zhang DC, Zhang RG, Wang LJ. Value of radiotherapy after radical surgery for esophageal carcinoma: a report of 495 patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;75:331–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
