Designing anti-inflammatory drugs from parasitic worms: a synthetic small molecule analogue of the Acanthocheilonema viteae product ES-62 prevents development of collagen-induced arthritis
- PMID: 24228757
- PMCID: PMC4125414
- DOI: 10.1021/jm401251p
Designing anti-inflammatory drugs from parasitic worms: a synthetic small molecule analogue of the Acanthocheilonema viteae product ES-62 prevents development of collagen-induced arthritis
Abstract
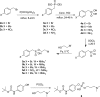
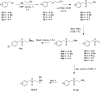
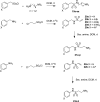
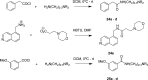
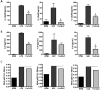
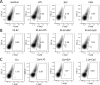
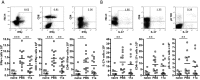
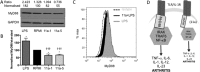
In spite of increasing evidence that parasitic worms may protect humans from developing allergic and autoimmune diseases and the continuing identification of defined helminth-derived immunomodulatory molecules, to date no new anti-inflammatory drugs have been developed from these organisms. We have approached this matter in a novel manner by synthesizing a library of drug-like small molecules based upon phosphorylcholine, the active moiety of the anti-inflammatory Acanthocheilonema viteae product, ES-62, which as an immunogenic protein is unsuitable for use as a drug. Following preliminary in vitro screening for inhibitory effects on relevant macrophage cytokine responses, a sulfone-containing phosphorylcholine analogue (11a) was selected for testing in an in vivo model of inflammation, collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). Testing revealed that 11a was as effective as ES-62 in protecting DBA/1 mice from developing CIA and mirrored its mechanism of action in downregulating the TLR/IL-1R transducer, MyD88. 11a is thus a novel prototype for anti-inflammatory drug development.
Figures





References
-
- de Silva N. R.; Brooker S.; Hotez P. J.; Montresor A.; Engels D.; Savioli L. Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections: Updating the Global Picture. Trends Parasitol. 2003, 19, 547–551. - PubMed
-
- Harnett W.; Grainger M.; Kapil A.; Worms M. J.; Parkhouse R. M. E. Origin, Kinetics of Circulation and Fate in Vivo of the Major Excretory–Secretory Product of Acanthocheilonema Viteae. Parasitol. Today 1989, 99, 229–239. - PubMed
-
- Goodridge H. S.; Marshall F. A.; Else K. J.; Houston K. M.; Egan C.; Al-Riyami L.; Liew F. Y.; Harnett W.; Harnett M. M. Immunomodulation via Novel Use of TLR4 by the Filarial Nematode Phosphorylcholine-Containing Secreted Product, ES-62. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 284–293. - PubMed
-
- Goodridge H. S.; McGuiness S.; Houston K. M.; Egan C. A.; Al-Riyami L.; Alcocer M. J.; Harnett M. M.; Harnett W. Phosphorylcholine Mimics the Effects of ES-62 on Macrophages and Dendritic Cells. Parasite Immunol. 2007, 29, 127–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

