Improved synthesis of carbon-clad silica stationary phases
- PMID: 24228897
- PMCID: PMC4295648
- DOI: 10.1021/ac401986j
Improved synthesis of carbon-clad silica stationary phases
Abstract
Previously, we described a novel method for cladding elemental carbon onto the surface of catalytically activated silica by a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method using hexane as the carbon source and its use as a substitute for carbon-clad zirconia.1,2 In that method, we showed that very close to exactly one uniform monolayer of Al (III) was deposited on the silica by a process analogous to precipitation from homogeneous solution in order to preclude pore blockage. The purpose of the Al(III) monolayer is to activate the surface for subsequent CVD of carbon. In this work, we present an improved procedure for preparing the carbon-clad silica (denoted CCSi) phases along with a new column packing process. The new method yields CCSi phases having better efficiency, peak symmetry, and higher retentivity compared to carbon-clad zirconia. The enhancements were achieved by modifying the original procedure in three ways: First, the kinetics of the deposition of Al(III) were more stringently controlled. Second, the CVD chamber was flushed with a mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen gas during the carbon cladding process to minimize generation of polar sites by oxygen incorporation. Third, the fine particles generated during the CVD process were exhaustively removed by flotation in an appropriate solvent.
Figures


 ) versus the untreated phase (
) versus the untreated phase ( ). T=40 °C, F=0.4 mL/min, 80%H2O:20%ACN. Both columns are packed using the same procedure given in the experimental section. The ratio of B/A tailing factor (at 10% of peak height) for the peaks on the hydrogen- treated phase versus untreated phase are shown in parenthesis respectively for each peak: nitrobutane (1.92, 2.16), nitropentane (1.85, 2.36), nitrohexane (2.59, 3.46). Plate counts on the peaks on the hydrogen-treated phase versus untreated phase are shown in parenthesis respectively for each peak: nitrobutane (3600,2800), nitropentane (5100,3700), nitrohexane (4500,2670)
). T=40 °C, F=0.4 mL/min, 80%H2O:20%ACN. Both columns are packed using the same procedure given in the experimental section. The ratio of B/A tailing factor (at 10% of peak height) for the peaks on the hydrogen- treated phase versus untreated phase are shown in parenthesis respectively for each peak: nitrobutane (1.92, 2.16), nitropentane (1.85, 2.36), nitrohexane (2.59, 3.46). Plate counts on the peaks on the hydrogen-treated phase versus untreated phase are shown in parenthesis respectively for each peak: nitrobutane (3600,2800), nitropentane (5100,3700), nitrohexane (4500,2670)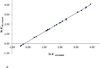
 alkyl benzenes (benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, p-xylene, n-propylbenzene, n-butylbenzene, naphthalene),
alkyl benzenes (benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, p-xylene, n-propylbenzene, n-butylbenzene, naphthalene),  nitro compounds (nitrobenzene, p-nitrotoluene, p-nitrobenzyl chloride),
nitro compounds (nitrobenzene, p-nitrotoluene, p-nitrobenzyl chloride),  (N-benzylformamide, anisole, methylbenzoate, acetophenone, benzonitrile, benzophenone),
(N-benzylformamide, anisole, methylbenzoate, acetophenone, benzonitrile, benzophenone),  alcohols (benzylalcohol, phenol, 3-phenylpropanol, p-chlorophenol),
alcohols (benzylalcohol, phenol, 3-phenylpropanol, p-chlorophenol),  halogenated (bromobenzene, p-chlorotoluene, p-dichlorobenzene). Chromatographic conditions as in Figure 3A. The solid line is computed from Eq. 5.
halogenated (bromobenzene, p-chlorotoluene, p-dichlorobenzene). Chromatographic conditions as in Figure 3A. The solid line is computed from Eq. 5.
 alkyl benzenes (benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, p-xylene, n-propylbenzene, n-butylbenzene, naphthalene),
alkyl benzenes (benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, p-xylene, n-propylbenzene, n-butylbenzene, naphthalene),  nitro compounds (nitrobenzene, p-nitrotoluene, p-nitrobenzyl chloride),
nitro compounds (nitrobenzene, p-nitrotoluene, p-nitrobenzyl chloride),  (N-benzylformamide, anisole, methylbenzoate, acetophenone, benzonitrile, benzophenone),
(N-benzylformamide, anisole, methylbenzoate, acetophenone, benzonitrile, benzophenone),  alcohols (benzylalcohol, phenol, 3-phenylpropanol, p-chlorophenol),
alcohols (benzylalcohol, phenol, 3-phenylpropanol, p-chlorophenol),  halogenated (bromobenzene, p-chlorotoluene, p-dichlorobenzene). Chromatographic conditions as in Figure 3A. The solid line is computed from Eq. 5.
halogenated (bromobenzene, p-chlorotoluene, p-dichlorobenzene). Chromatographic conditions as in Figure 3A. The solid line is computed from Eq. 5.

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

