Managing HIV/hepatitis C co-infection in the era of direct acting antivirals
- PMID: 24228933
- PMCID: PMC4225604
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-234
Managing HIV/hepatitis C co-infection in the era of direct acting antivirals
Abstract
Morbidity and mortality from co-morbid hepatitis C (HCV) infection in HIV co-infected patients are increasing; hence, the management of hepatitis co-infection in HIV is now one of the most important clinical challenges. Therefore, the development of direct acting antivirals (DAAs) for treatment of HCV has been eagerly awaited to hopefully improve HCV treatment outcome in co-infected individuals. Indeed, the availability of the first HCV protease inhibitors (PI) boceprevir and telaprevir for HCV genotype 1 patients has changed the gold standard of treating hepatitis C allowing for substantially improved HCV cure rates under triple HCV-PI/pegylated interferon/ribavirin therapy. Moreover, numerous other new DAAs are currently being studied in co-infected patient populations, also exploring shorter treatment durations and interferon-free treatment approaches promising much easier and better tolerated treatment regimens in the near future. Nevertheless, numerous challenges remain, including choice of patients to treat, potential for drug-drug interactions and overlapping toxicities between HIV and HCV therapy. The dramatically improved rates of HCV cure under new triple therapy, however, warrant evaluation of these new treatment options for all co-infected patients.
Figures
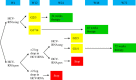
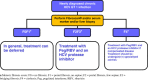

References
-
- Weber R, Ruppik M, Rickenbach M, Spoerri A, Furrer H, Battegay M, Cavassini M, Calmy A, Bernasconi E, Schmid P, Flepp M, Kowalska J, Ledergerber B. Swiss HIV Cohort Study (SHCS) Decreasing mortality and changing patterns of causes of death in the Swiss HIV Cohort Study. HIV Med. 2013;14:195–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1293.2012.01051.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rockstroh JK, Mocroft A, Soriano V, Tural C, Losso MH, Horban A, Kirk O, Phillips A, Ledergerber B, Lundgren J. EuroSIDA Study Group. Influence of hepatitis C virus infection on HIV-1 disease progression and response to highly active antiretroviral therapy. J Infect Dis. 2005;192:992–1002. doi: 10.1086/432762. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Soriano V, Mocroft A, Rockstroh J, Ledergerber B, Knysz B, Chaplinskas S, Peters L, Karlsson A, Katlama C, Toro C, Kupfer B, Vogel M, Lundgren J. EuroSIDA Study Group. Spontaneous viral clearance, viral load, and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus (HCV) in HIV-infected patients with anti-HCV antibodies in Europe. J Infect Dis. 2008;198:1337–1344. doi: 10.1086/592171. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rockstroh JK, Spengler U, Sudhop T, Ewig S, Theisen A, Hammerstein U, Bierhoff E, Fischer HP, Oldenburg J, Brackmann HH, Sauerbruch T. Immunosuppression may lead to progression of hepatitis C virus-associated liver disease in hemophiliacs coinfected with HIV. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996;91:2563–2568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

