Azithromycin and cough-specific health status in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and chronic cough: a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 24229360
- PMCID: PMC3835397
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-14-125
Azithromycin and cough-specific health status in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and chronic cough: a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Macrolides reduce exacerbations in patients with COPD. Their effects on health status has not been assessed as primary outcome and is less clear. This study assessed the effects of prophylactic azithromycin on cough-specific health status in COPD-patients with chronic productive cough.
Methods: In this randomised controlled trial 84 patients met the eligibility criteria: age of ≥40 years, COPD GOLD stage ≥2 and chronic productive cough. The intervention-group (n = 42) received azithromycin 250 mg 3 times a week and the control-group (n = 42) received a placebo. Primary outcome was cough-specific health status at 12 weeks, measured with the Leicester Cough Questionnaire (LCQ). Secondary outcomes included generic and COPD-specific health status and exacerbations. Changes in adverse events and microbiology were monitored.
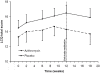
Results: Mean age of participants was 68 ± 10 years and mean FEV1 was 1.36 ± 0.47 L. The improvement in LCQ total score at 12 weeks was significantly greater with azithromycin (difference 1.3 ± 0.5, 95% CI 0.3;2.3, p = 0.01) and met the minimal clinically important difference. Similar results were found for the domain scores, and COPD-specific and generic health status questionnaires. Other secondary endpoints were non-significant. No imbalances in adverse events were found.
Conclusions: Prophylactic azithromycin improved cough-specific health status in COPD-patients with chronic productive cough to a clinically relevant degree.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01071161.
Figures

References
-
- Buist AS, McBurnie MA, Vollmer WM, Gillespie S, Burney P, Mannino DM, Menezes AM, Sullivan SD, Lee TA, Weiss KB, Jensen RL, Marks GB, Gulsvik A, Nizankowska-Mogilnicka E. International variation in the prevalence of COPD (the BOLD Study): a population-based prevalence study. Lancet. 2007;370:741–750. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61377-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rabe KF, Hurd S, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Buist SA, Calverley P, Fukuchi Y, Jenkins C, Rodriguez-Roisin R, van WC, Zielinski J. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176:532–555. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200703-456SO. - DOI - PubMed
-
- de MR, Accordini S, Cerveri I, Corsico A, Anto JM, Kunzli N, Janson C, Sunyer J, Jarvis D, Chinn S, Vermeire P, Svanes C, ckermann-Liebrich U, Gislason T, Heinrich J, Leynaert B, Neukirch F, Schouten JP, Wjst M, Burney P. Incidence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in a cohort of young adults according to the presence of chronic cough and phlegm. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:32–39. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200603-381OC. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

