Development and translation of histotripsy: current status and future directions
- PMID: 24231530
- PMCID: PMC3974592
- DOI: 10.1097/MOU.0000000000000001
Development and translation of histotripsy: current status and future directions
Abstract
Purpose of review: The aim of this article is to outline the initial development of histotripsy, a noninvasive image-guided focused ultrasound technology that mechanically homogenizes targeted tissues and to describe the results of preclinical translational research directed toward urologic applications.
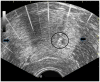
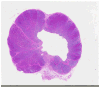
Recent findings: Histotripsy tissue ablation is based on initiation and control of acoustic cavitation at a target point within the body. This unique mechanical mechanism of action is distinct when compared with conventional thermal ablative modalities. Features of histotripsy (nonthermal, noninvasive, high precision, real-time monitoring/feedback, and tissue liquefaction) have prompted assessment of this technology as a potential ablative therapy for a number of organs and disease processes.
Summary: Ongoing research efforts to apply histotripsy to preclinical models of benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostate cancer, renal masses, and renal calculi have resulted in enhanced understanding of cavitation bioeffects, refinement of treatment systems, strategies to enhance treatment efficiency, and initiation of a pilot human clinical trial to assess the safety of histotripsy for benign prostatic hyperplasia therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: WWR has equity, royalty, and consulting interests in HistoSonics, Inc. He is the principal investigator on a sponsored research grant from HistoSonics, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Parsons JE, Cain CA, Abrams GD, Fowlkes JB. Pulsed cavitational ultrasound therapy for controlled tissue homogenization. Ultrasound in Med & Biol. 2006;32:115–29. - PubMed
-
- Xu Z, Raghavan M, Hall TL, et al. Evolution of bubble clouds induced by pulsed cavitational ultrasound therapy – histotripsy. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2008;55:1122–32. - PubMed
-
- Roberts WW, Hall TL, Ives K, et al. Pulsed cavitational ultrasound: A noninvasive technology for controlled tissue ablation (histotripsy) in the rabbit kidney. J Urol. 2006;175:734–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

