Discovery of a novel activator of 5-lipoxygenase from an anacardic acid derived compound collection
- PMID: 24231650
- PMCID: PMC4017091
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.10.015
Discovery of a novel activator of 5-lipoxygenase from an anacardic acid derived compound collection
Abstract
Lipoxygenases (LOXs) and cyclooxygenases (COXs) metabolize poly-unsaturated fatty acids into inflammatory signaling molecules. Modulation of the activity of these enzymes may provide new approaches for therapy of inflammatory diseases. In this study, we screened novel anacardic acid derivatives as modulators of human 5-LOX and COX-2 activity. Interestingly, a novel salicylate derivative 23a was identified as a surprisingly potent activator of human 5-LOX. This compound showed both non-competitive activation towards the human 5-LOX activator adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and non-essential mixed type activation against the substrate linoleic acid, while having no effect on the conversion of the substrate arachidonic acid. The kinetic analysis demonstrated a non-essential activation of the linoleic acid conversion with a KA of 8.65 μM, αKA of 0.38μM and a β value of 1.76. It is also of interest that a comparable derivative 23d showed a mixed type inhibition for linoleic acid conversion. These observations indicate the presence of an allosteric binding site in human 5-LOX distinct from the ATP binding site. The activatory and inhibitory behavior of 23a and 23d on the conversion of linoleic compared to arachidonic acid are rationalized by docking studies, which suggest that the activator 23a stabilizes linoleic acid binding, whereas the larger inhibitor 23d blocks the enzyme active site.
Keywords: Allosteric binding; Anacardic acid; Cyclooxygenase-2; Enzyme kinetics; Human 5-lipoxygenase.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript. RW, PAMK and NE synthesized the molecules and performed the biochemical analysis. MPB and CJC performed and analyzed the docking studies and were supported by grant R01GM097082-01 from the National Institutes of Health. HJH and FJD supervised the research. RW and FJD wrote the manuscript.
Figures



















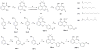
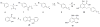


Similar articles
-
Anacardic acid derived salicylates are inhibitors or activators of lipoxygenases.Bioorg Med Chem. 2012 Aug 15;20(16):5027-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.06.019. Epub 2012 Jun 21. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22789707
-
Lipoxygenase inhibitory activity of anacardic acids.J Agric Food Chem. 2005 Jun 1;53(11):4350-4. doi: 10.1021/jf048184e. J Agric Food Chem. 2005. PMID: 15913294
-
Exploration of binding site pattern in arachidonic acid metabolizing enzymes, Cyclooxygenases and Lipoxygenases.BMC Res Notes. 2015 Apr 16;8:152. doi: 10.1186/s13104-015-1101-4. BMC Res Notes. 2015. PMID: 25886468 Free PMC article.
-
5-Lipoxygenase as a drug target: A review on trends in inhibitors structural design, SAR and mechanism based approach.Bioorg Med Chem. 2019 Sep 1;27(17):3745-3759. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2019.06.040. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Bioorg Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31331653 Review.
-
Discovery of ML355, a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of Human 12-Lipoxygenase.2013 Apr 12 [updated 2014 Sep 18]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. 2013 Apr 12 [updated 2014 Sep 18]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. PMID: 25506969 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Chalcone-Thiazole Hybrids: Rational Design, Synthesis, and Lead Identification against 5-Lipoxygenase.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2019 Sep 9;10(10):1415-1422. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00193. eCollection 2019 Oct 10. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2019. PMID: 31620227 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of a small molecule that activates thiosulfate sulfurtransferase and stimulates mitochondrial respiration.Protein Sci. 2023 Nov;32(11):e4794. doi: 10.1002/pro.4794. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 37800277 Free PMC article.
-
Docking Studies on Biomolecules from Marine Microalga Skeletonema costatum Against Hemolysin Protein of Bioluminescence Disease-Causing Vibrio harveyi.Curr Microbiol. 2023 Jul 18;80(9):290. doi: 10.1007/s00284-023-03372-3. Curr Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37462776
-
Uncoupling conformational states from activity in an allosteric enzyme.Nat Commun. 2017 Aug 7;8(1):203. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00224-0. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28781362 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Anti-Inflammatory Pathways to Treat Diabetes-Induced Neuropathy by 6-Hydroxyflavanone.Nutrients. 2023 May 30;15(11):2552. doi: 10.3390/nu15112552. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37299516 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Research Materials

