mTOR inhibition alleviates mitochondrial disease in a mouse model of Leigh syndrome
- PMID: 24231806
- PMCID: PMC4055856
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1244360
mTOR inhibition alleviates mitochondrial disease in a mouse model of Leigh syndrome
Abstract
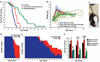
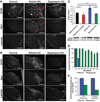
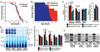
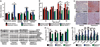
Mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to numerous health problems, including neurological and muscular degeneration, cardiomyopathies, cancer, diabetes, and pathologies of aging. Severe mitochondrial defects can result in childhood disorders such as Leigh syndrome, for which there are no effective therapies. We found that rapamycin, a specific inhibitor of the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway, robustly enhances survival and attenuates disease progression in a mouse model of Leigh syndrome. Administration of rapamycin to these mice, which are deficient in the mitochondrial respiratory chain subunit Ndufs4 [NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) Fe-S protein 4], delays onset of neurological symptoms, reduces neuroinflammation, and prevents brain lesions. Although the precise mechanism of rescue remains to be determined, rapamycin induces a metabolic shift toward amino acid catabolism and away from glycolysis, alleviating the buildup of glycolytic intermediates. This therapeutic strategy may prove relevant for a broad range of mitochondrial diseases.
Figures
Comment in
-
Neurometabolic disease: Treating mitochondrial diseases with mTOR inhibitors--a potential treatment for Leigh syndrome?Nat Rev Neurol. 2014 Jan;10(1):2. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2013.251. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24296657 No abstract available.
-
Medicine. A common pathway for a rare disease?Science. 2013 Dec 20;342(6165):1453-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1248449. Science. 2013. PMID: 24357304 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

