Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: from cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy
- PMID: 24232462
- PMCID: PMC4077177
- DOI: 10.1038/nri3552
Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: from cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy
Abstract
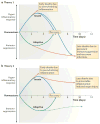
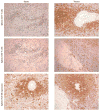
Sepsis - which is a severe life-threatening infection with organ dysfunction - initiates a complex interplay of host pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory processes. Sepsis can be considered a race to the death between the pathogens and the host immune system, and it is the proper balance between the often competing pro- and anti-inflammatory pathways that determines the fate of the individual. Although the field of sepsis research has witnessed the failure of many highly touted clinical trials, a better understanding of the pathophysiological basis of the disorder and the mechanisms responsible for the associated pro- and anti-inflammatory responses provides a novel approach for treating this highly lethal condition. Biomarker-guided immunotherapy that is administered to patients at the proper immune phase of sepsis is potentially a major advance in the treatment of sepsis and in the field of infectious disease.
Figures


References
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Moss M. The effect of age on the development and outcome of adult sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Cohen J, Opal S, Calandra T. Sepsis studies need new direction. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12:503–5. - PubMed
-
- Wenzel RP, Edmond MB. Septic shock--evaluating another failed treatment. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2122–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

