Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) regulates the function of CLOCK protein by direct phosphorylation
- PMID: 24235147
- PMCID: PMC3873547
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.494856
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) regulates the function of CLOCK protein by direct phosphorylation
Abstract
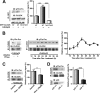
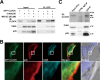
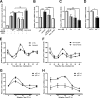
Circadian rhythm is a biological rhythm governing physiology and behavior with a period of ∼24 h. At the molecular level, circadian output is controlled by a molecular clock composed of positive and negative feedback loops in transcriptional and post-translational processes. CLOCK is a transcription factor known as a central component of the molecular clock feedback loops generating circadian oscillation. Although CLOCK is known to undergo multiple post-translational modifications, the knowledge of their entities remains limited. Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) is a proline-directed serine-threonine kinase that is involved in various neuronal processes. Here, we report that Cdk5 is a novel regulator of CLOCK protein. Cdk5 phosphorylates CLOCK at the Thr-451 and Thr-461 residues in association with transcriptional activation of CLOCK. The Cdk5-dependent regulation of CLOCK function is mediated by alterations of its stability and subcellular distribution. These results suggest that Cdk5 is a novel regulatory component of the core molecular clock machinery.
Keywords: CDK (Cyclin-dependent Kinase); CLOCK; Cdk5; Circadian Rhythms; Clock Genes; Molecular Clock; Neuroscience; Protein Phosphorylation.
Figures



References
-
- Reppert S. M., Weaver D. R. (2001) Molecular analysis of mammalian circadian rhythms. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 63, 647–676 - PubMed
-
- Schibler U., Sassone-Corsi P. (2002) A web of circadian pacemakers. Cell 111, 919–922 - PubMed
-
- Balsalobre A., Marcacci L., Schibler U. (2000) Multiple signaling pathways elicit circadian gene expression in cultured Rat-1 fibroblasts. Curr. Biol. 10, 1291–1294 - PubMed
-
- Yagita K., Tamanini F., van Der Horst G. T., Okamura H. (2001) Molecular mechanisms of the biological clock in cultured fibroblasts. Science 292, 278–281 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

