B-type natriuretic peptide and prognosis of end-stage renal disease: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 24236118
- PMCID: PMC3827377
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079302
B-type natriuretic peptide and prognosis of end-stage renal disease: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The prognostic importance of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) or N-terminal pro BNP (NT-proBNP) in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) remains controversial.
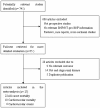
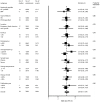
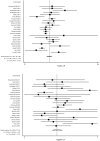
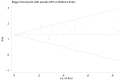
Methodology/principal findings: We conducted an unrestricted search from the MEDLINE and EMBASE in all languages that were published between 1966 and Augest2013. Twenty-seven long-term prospective studies met our inclusion criterias. From the pooled analysis, elevated BNP/NT-proBNP was significantly associated with increased all cause mortality [odds ratio (OR), 3.85; 95% CI, 3.11 to 4.75], cardiovascular mortality (OR, 4.05; 95% CI, 2.53 to 6.84), and cardiovascular events (OR, 7.02; 95% CI, 2.21 to 22.33). The funnel plot showed no evidence of publication bias. The corresponding pooled positive and negative likelihood ratio for prediction of all cause mortality were 1.86 (95% CI, 1.66 to 2.08) and 0.48 (95% CI, 0.42 to 0.55), respectively.
Conclusions/significance: BNP/NT-proBNP is a promising prognostic tool to risk-stratify the patients with ESRD. Further investigations are warranted to elucidate the specific pathogenic mechanisms and the impact of other potential prognostic factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of NT-proBNP and BNP With Future Clinical Outcomes in Patients With ESKD: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Am J Kidney Dis. 2020 Aug;76(2):233-247. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.12.017. Epub 2020 May 6. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020. PMID: 32387090
-
Prognostic value of brain natriuretic peptide in noncardiac surgery: a meta-analysis.Anesthesiology. 2009 Aug;111(2):311-9. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181aaeb11. Anesthesiology. 2009. PMID: 19602961 Review.
-
The Molar Ratio of N-terminal pro-B-type Natriuretic Peptide/B-type Natriuretic Peptide for Heart Failure-related Events in Stable Outpatients with Cardiovascular Risk Factors.Intern Med. 2018 Sep 15;57(18):2621-2630. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0471-17. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29709934 Free PMC article.
-
Combining the use of amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and B-type natriuretic peptide in the prognosis of hospitalized heart failure patients.Clin Chim Acta. 2019 Apr;491:8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.12.025. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Clin Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 30594544
-
Changes of natriuretic peptides predict hospital admissions in patients with chronic heart failure: a meta-analysis.JACC Heart Fail. 2014 Apr;2(2):148-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2013.11.007. JACC Heart Fail. 2014. PMID: 24720923 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute Coronary Syndromes in Chronic Kidney Disease: Clinical and Therapeutic Characteristics.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Mar 8;56(3):118. doi: 10.3390/medicina56030118. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 32182690 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Cardiovascular Risk After Radiotherapy in Women With Breast Cancer.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 May 21;6(5):e005633. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.005633. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28529208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Routinely measured cardiac troponin I and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide as predictors of mortality in haemodialysis patients.ESC Heart Fail. 2022 Apr;9(2):1138-1151. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13784. Epub 2022 Jan 13. ESC Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 35026869 Free PMC article.
-
N-terminal prohormone B-type natriuretic peptide variability acts as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with cardiorenal syndrome type 2.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):12407-12419. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2005219. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34905428 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular risk in renal transplant recipients.J Nephrol. 2019 Jun;32(3):389-399. doi: 10.1007/s40620-018-0549-4. Epub 2018 Nov 7. J Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30406606 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Herzog CA, Ma JZ, Collins AJ (1998) Poor long-term survival after acute myocardial infarction among patients on long-term dialysis. N Engl J Med 339: 799–805. - PubMed
-
- Daniels LB, Maisel AS (2007) Natriuretic peptides. J Am Coll Cardiol 50: 2357–2368. - PubMed
-
- Dickstein K, Cohen-Solal A, Filippatos G, McMurray JJ, Ponikowski P, et al. (2008) ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association of the ESC (HFA) and endorsed by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM). Eur J Heart Fail 10: 933–989. - PubMed
-
- Madsen LH, Ladefoged S, Corell P, Schou M, Hildebrandt PR, et al. (2007) N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide predicts mortality in patients with end-stage renal disease in hemodialysis. Kidney Int 71: 548–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

