A shortened Barnes maze protocol reveals memory deficits at 4-months of age in the triple-transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 24236177
- PMCID: PMC3827415
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080355
A shortened Barnes maze protocol reveals memory deficits at 4-months of age in the triple-transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
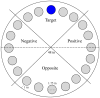
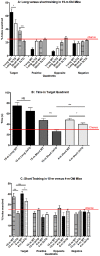
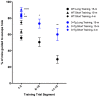
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that manifests as memory loss, cognitive dysfunction, and dementia. Animal models of Alzheimer's disease have been instrumental in understanding the underlying pathological mechanism and in evaluation of potential therapies. The triple transgenic (3 × Tg) mouse model of AD is unique because it recapitulates both pathologic hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease--amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. The earliest cognitive deficits in this model have been shown at 6-m of age by most groups, necessitating aging of the mice to this age before initiating evaluation of the cognitive effects of therapies. To assess cognitive deficits in the 3 × Tg mice, originally we employed a typical Barnes maze protocol of 15 training trials, but found no significant deficits in aged mice. Therefore, we shortened the protocol to include only 5 training trials to increase difficulty. We found cognitive deficits using this protocol using mainly measures from the probe day, rather than the training trials. This also decreased the effort involved with data analysis. We compared 3 × Tg and wild-type mice at 4-m- and 15-m of age using both the original, long training, and the short training paradigms. We found that differences in learning between 3 × Tg and wild-type mice disappeared after the 4(th) training trial. Measures of learning and memory on the probe day showed significant differences between 3 × Tg and wild-type mice following the short, 5-training trial protocol but not the long, 15-training trial protocol. Importantly, we detected cognitive dysfunction already at 4-m of age in 3 × Tg mice using the short Barnes-maze protocol. The ability to test learning and memory in 4-m old 3 × Tg mice using a shortened Barnes maze protocol offers considerable time and cost savings and provides support for the utilization of this model at pre-pathology stages for therapeutic studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Barnes CA (1979) Memory deficits associated with senescence: a neurophysiological and behavioral study in the rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol 93: 74–104. - PubMed
-
- O′Leary TP, Brown RE (2009) Visuo-spatial learning and memory deficits on the Barnes maze in the 16-month-old APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Behavioural brain research 201: 120–127. - PubMed
-
- Frazer ME, Hughes JE, Mastrangelo MA, Tibbens JL, Federoff HJ, et al. (2008) Reduced pathology and improved behavioral performance in Alzheimer's disease mice vaccinated with HSV amplicons expressing amyloid-β and interleukin-4. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 16: 845–853. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

