The caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide decreases phosphatidylglycerol levels and inhibits calcium-induced differentiation in mouse keratinocytes
- PMID: 24236206
- PMCID: PMC3827482
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080946
The caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide decreases phosphatidylglycerol levels and inhibits calcium-induced differentiation in mouse keratinocytes
Abstract
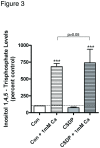
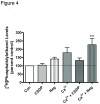
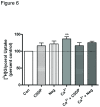
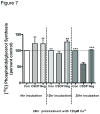
Phospholipase D2 (PLD2) has been found localized in low-density caveolin-rich membrane microdomains. Our previous study suggested that PLD2 and aquaporin 3 (AQP3) interact in these domains to inhibit keratinocyte proliferation and promote differentiation by cooperating to produce phosphatidylglycerol. To examine the effect of membrane microdomain localization on the PLD2/AQP3 signaling module and keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation, we treated mouse keratinocytes with 3 µM cell-permeable caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide or a negative control peptide and stimulated cell differentiation using a moderately elevated extracellular calcium concentration (125 uM) to maximally promote differentiation and phosphatidylglycerol production. Cell proliferation, differentiation, total PLD activity, phosphatidylglycerol levels, and AQP3 activity were monitored. The caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide itself had no effect on phosphatidylglycerol levels or keratinocyte proliferation or differentiation but prevented the changes induced by a moderately elevated calcium concentration, whereas a negative control did not. The caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide had little effect on total PLD activity or glycerol uptake (AQP3 activity). We conclude that the caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide disrupts the functional association between AQP3 and PLD2 and prevents both the inhibited proliferation and the stimulated differentiation in response to elevated extracellular calcium levels. The interaction of caveolin-1 and PLD2 is indirect (i.e., lipid mediated); together with the proliferation-promoting effects of caveolin-1 knockout on epidermal keratinocytes, we propose that the caveolin-1 scaffolding domain pepetide exerts a dominant-negative effect on caveolin-1 to alter lipid rafts in these cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
A potential role for the phospholipase D2-aquaporin-3 signaling module in early keratinocyte differentiation: production of a phosphatidylglycerol signaling lipid.J Invest Dermatol. 2007 Dec;127(12):2823-31. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700921. Epub 2007 Jun 28. J Invest Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17597824
-
Aquaporin-3 re-expression induces differentiation in a phospholipase D2-dependent manner in aquaporin-3-knockout mouse keratinocytes.J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Feb;135(2):499-507. doi: 10.1038/jid.2014.412. Epub 2014 Sep 18. J Invest Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25233074 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporin 3 colocates with phospholipase d2 in caveolin-rich membrane microdomains and is downregulated upon keratinocyte differentiation.J Invest Dermatol. 2003 Dec;121(6):1487-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1747.2003.12614.x. J Invest Dermatol. 2003. PMID: 14675200
-
Aquaporin-3 in keratinocytes and skin: its role and interaction with phospholipase D2.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2011 Apr 15;508(2):138-43. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2011.01.014. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2011. PMID: 21276418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphatidylglycerol to Treat Chronic Skin Wounds in Diabetes.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 14;15(5):1497. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051497. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242739 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of caveolin-1 in skin diseases.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 30;13:1035451. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1035451. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36532050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phospholipase D2 loss results in increased blood pressure via inhibition of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase pathway.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 22;7(1):9112. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09852-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28831159 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid rafts and detergent-resistant membranes in epithelial keratinocytes.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1195:133-44. doi: 10.1007/7651_2014_71. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24504930 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptides enhance anti-inflammatory effect of heme oxygenase-1 through interrupting its interact with caveolin-1.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 20;8(25):40104-40114. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16676. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28402952 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 Scaffolding Domain Peptides Alleviate Liver Fibrosis by Inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad Signaling in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 11;19(6):1729. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061729. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29891777 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

