Novel adjunctive therapies for the treatment of tuberculosis
- PMID: 24236454
- PMCID: PMC4484774
- DOI: 10.2174/1566524013666131118112431
Novel adjunctive therapies for the treatment of tuberculosis
Abstract
Despite significant efforts to control tuberculosis (TB), the disease remains a major global threat, with an estimated 8.6 million new cases and 1.3 million deaths in 2012 alone. Significant treatment challenges include HIV co-infection, the dramatic rise of multidrug-resistant TB and the vast reservoir of latently infected individuals, who will develop active disease years after the initial infection. The long duration of chemotherapy also remains a major barrier to effective large scale treatment of TB. Significant advances are being made in the development of shorter and effective TB drug regimens and there is growing evidence that host-directed and "non-antimicrobial" pathogen-directed therapies, could serve as novel approaches to enhance TB treatments. This review highlights the rationale for using these therapies and summarizes some of the progress in this field.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have a commercial or other association that might pose a conflict of interest.
Figures

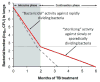
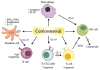
References
-
- WHO. [Accessed: November 28, 2013];Global tuberculosis report. 2013 Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/91355/1/9789241564656_eng.pdf.
-
- Dye C, Scheele S, Dolin P, Pathania V, Raviglione MC. Consensus statement. Global burden of tuberculosis: estimated incidence, prevalence, and mortality by country. WHO Global Surveillance and Monitoring Project. JAMA. 1999;282(7):677–86. - PubMed
-
- Stead WW. Pathogenesis of a first episode of chronic pulmonary tuberculosis in man: recrudescence of residuals of the primary infection or exogenous reinfection? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967;95(5):729–45. - PubMed
-
- Podlekareva DN, Panteleev AM, Grint D, et al. Short and long term mortality and causes of death in HIV/TB patients in Europe. Eur Respir J. 2013 epub ahead of print. - PubMed
-
- Grosset JH, Singer TG, Bishai WR. New drugs for the treatment of tuberculosis: hope and reality. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2012;16(8):1005–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
