Acquired aplastic anemia in children
- PMID: 24237973
- PMCID: PMC3894991
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pcl.2013.08.011
Acquired aplastic anemia in children
Abstract
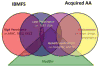
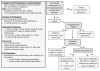
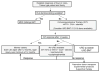
This article provides a practice-based and concise review of the etiology, diagnosis, and management of acquired aplastic anemia in children. Bone marrow transplantation, immunosuppressive therapy, and supportive care are discussed in detail. The aim is to provide the clinician with a better understanding of the disease and to offer guidelines for the management of children with this uncommon yet serious disorder.
Keywords: Acquired aplastic anemia; Bone marrow failure; Bone marrow transplant for severe aplastic anemia in children; Immune-mediated aplastic anemia; Immunosuppressive therapy for severe aplastic anemia in children.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Bessler: None
Dr. Hartung: None
Dr. Olson: None
Figures


References
-
- Camitta BM, Rappeport JM, Parkman R, et al. Selection of patients for bone marrow transplantation in severe aplastic anemia. Blood. 1975;45:355–363. - PubMed
-
- Bacigalupo A, Hows J, Gluckman E, et al. Bone marrow transplantation (BMT) versus immunosuppression for the treatment of severe aplastic anaemia (SAA): a report of the EBMT SAA working party. Br J Haematol. 1988;70:177–182. - PubMed
-
- Bessler M, Mason P, Link D, et al. Inherited bone marrrow failure syndromes. In: DGN, SHO, DG, et al., editors. Nathans and Oski’s Hematology of infancy and childhood. 8. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Co; 2014.
-
- Baumann I, Niemeyer C, Bennett J, et al. Childhood myelodysplastic syndrome. In: Swerdlow S, EC, NLH, et al., editors. WHO classification of tumors of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissue. Vol. 2. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2008. pp. 104–107.
-
- Baumann I, Fuhrer M, Behrendt S, et al. Morphological differentiation of severe aplastic anaemia from hypocellular refractory cytopenia of childhood: reproducibility of histopathological diagnostic criteria. Histopathology. 2012;61:10–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

