Factors affecting pleural fluid adenosine deaminase level and the implication on the diagnosis of tuberculous pleural effusion: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 24238276
- PMCID: PMC3835552
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-546
Factors affecting pleural fluid adenosine deaminase level and the implication on the diagnosis of tuberculous pleural effusion: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Adenosine deaminase (ADA) is useful in the diagnosis of tuberculous pleural effusion (TPE). This study aims to determine the factors affecting pleural fluid ADA levels and to establish the optimal ADA levels for diagnosis of TPE for different age groups.
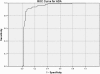
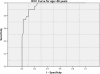
Methods: This was a retrospective study from January 2007 to October 2011. One hundred and sixty patients who had pleural fluid ADA performed for investigation of pleural effusion were analyzed. Variables examined included demographics, pleural fluid characteristics and peripheral blood counts. The ADA cut-offs according to age were selected using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
Results: The mean pleural fluid ADA was significantly higher in the TPE group (100 ± 35 IU/L) compared to non TPE patients (30 ± 37 IU/L). There was significant correlation between pleural fluid ADA and age, pleural fluid protein, LDH, and fluid absolute lymphocyte count. The strongest correlation was seen with age (r = -0.621). For patients ≤ 55 years old the ROC for ADA had area under curve (AUC) of 0.887. A pleural fluid ADA of 72 IU/L had sensitivity of 95.1%, specificity of 87.5%, positive predictive value (PPV) of 95.1% and negative predictive value (NPV) of 87.5% for the diagnosis of TPE. For patients > 55 years old the AUC is 0.959. ADA of 26 IU/L had a sensitivity of 94.7%, specificity of 80.4%, PPV of 62% and NPV of 97.8%.
Conclusions: There is a significant negative correlation between pleural fluid ADA and age. For older patients, a lower ADA cut-off should be used to exclude TPE.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The pleural fluid lactate dehydrogenase/adenosine deaminase ratio differentiates between tuberculous and parapneumonic pleural effusions.BMC Pulm Med. 2017 Dec 4;17(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12890-017-0526-z. BMC Pulm Med. 2017. PMID: 29202740 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of age on the diagnostic accuracy of soluble biomarkers for tuberculous pleural effusion: a post hoc analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2020 Jun 22;20(1):178. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-01219-2. BMC Pulm Med. 2020. PMID: 32571326 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive role of adenosine deaminase for differential diagnosis of tuberculosis and malignant pleural effusion in Turkey.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011;12(2):419-23. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011. PMID: 21545206
-
Adenosine deaminase for diagnosis of tuberculous pleural effusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2019 Mar 26;14(3):e0213728. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213728. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30913213 Free PMC article.
-
IgG4-related pleural effusion with high adenosine deaminase levels: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Mar 19;100(11):e25162. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025162. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33726002 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Complement regulatory proteins: Candidate biomarkers in differentiating tuberculosis pleural effusion.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 3;14:1073884. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1073884. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36820087 Free PMC article.
-
Repeatability of pleural adenosine deaminase measurements in diagnostic evaluation of pleural effusions.J Clin Lab Anal. 2018 Jun;32(5):e22371. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22371. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Clin Lab Anal. 2018. PMID: 29218743 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with negative pleural adenosine deaminase results in the diagnosis of childhood pleural tuberculosis.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 May 25;21(1):473. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06209-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34034670 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Venn's diagram in the diagnosis of pleural tuberculosis using IFN-γ, IP-10 and adenosine deaminase.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 27;13(8):e0202481. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202481. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30148839 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Application of Adenosine Deaminase and γ-Interferon Release Assay in Pleural Fluid for the Diagnosis of Tuberculous Pleural Effusion in Patients Over 40 Years Old.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Feb 17;16:1009-1018. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S400838. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 36824067 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Light RW. Pleural Diseases. 5. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials