Ectopic endometrium-derived leptin produces estrogen-dependent chronic pain in a rat model of endometriosis
- PMID: 24239717
- PMCID: PMC3947893
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.11.008
Ectopic endometrium-derived leptin produces estrogen-dependent chronic pain in a rat model of endometriosis
Abstract
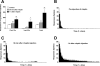
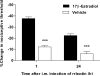
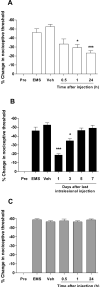
Endometriosis pain is a very common and extremely disabling condition whose mechanism is still poorly understood. While increased levels of leptin have been reported in patients with endometriosis, their contribution to endometriosis pain has not been explored. Using a rodent model of endometriosis we provide evidence for an estrogen-dependent contribution of leptin in endometriosis-induced pain. Rats implanted with autologous uterine tissue onto the gastrocnemius muscle developed endometriosis-like lesions and local chronic pain. Compared to eutopic uterine tissue, leptin mRNA and protein were up-regulated in the endometriosis-like lesions. Intramuscular injection of recombinant leptin in naive rats produced dose-dependent local mechanical hyperalgesia and nociceptor sensitization to mechanical stimulation. Ovariectomy attenuated the mechanical hyperalgesia induced by recombinant leptin, in rats treated with vehicle compared to those treated with 17β-estradiol replacement, at 1 and 24 h after leptin injection. Finally, intralesional injections of a pegylated leptin receptor (Ob-R) antagonist or of an inhibitor of Janus kinase2, which transduces the Ob-R signal, markedly attenuated pain in the endometriosis model. Taken together these data support the hypothesis that leptin, generated in ectopic endometrial lesions produces mechanical hyperalgesia by acting on nociceptors innervating the lesion. This sensitivity to leptin is dependent on estrogen levels. Thus, interventions targeting leptin signaling, especially in combination with interventions that lower estrogen levels, might be useful for the treatment of endometriosis pain.
Keywords: BSA; D-PBS; DRG; Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline; JAK2; Janus kinase2; Ob-R; RT-PCR; STAT3; bovine serum albumin; chronic pelvic pain; dorsal root ganglion; endometriosis; leptin; leptin receptor; mechanical hyperalgesia; nociceptor; ob gene; recombinant rat leptin; reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction; rrleptin; signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
Copyright © 2013 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

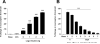
References
-
- Ainslie DA, Morris MJ, Wittert G, Turnbull H, Proietto J, Thorburn AW. Estrogen deficiency causes central leptin insensitivity and increased hypothalamic neuropeptide Y. International journal of obesity and related metabolic disorders : journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity. 2001;25:1680–1688. - PubMed
-
- Babaei A, Zarkesh-Esfahani SH, Bahrami E, Ross RJ. Restricted leptin antagonism as a therapeutic approach to treatment of autoimmune diseases. Hormones (Athens) 2011;10:16–26. - PubMed
-
- Barcz E, Milewski L, Radomski D, Dziunycz P, Kaminski P, Roszkowski PI, Malejczyk J. A relationship between increased peritoneal leptin levels and infertility in endometriosis. Gynecological endocrinology : the official journal of the International Society of Gynecological Endocrinology. 2008;24:526–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

